¶ Introduction
 From RepRapFirmware 3.6, Duet 3 mainboards 6HC, 6XD and Mini 5+ support RS485 serial data transmission standard and the Modbus RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) protocol. These can be used to interface with a wide range of devices, including sensors, relays, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) and other devices.
From RepRapFirmware 3.6, Duet 3 mainboards 6HC, 6XD and Mini 5+ support RS485 serial data transmission standard and the Modbus RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) protocol. These can be used to interface with a wide range of devices, including sensors, relays, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) and other devices.
Duet 3 Mainboard 6HC v1.02c and later, and Duet 3 Mainboard 6XD v1.02 and later, have an RS485 adapter built-in. For Mini 5+ and older versions of 6HC and 6XD, external RS485 transceivers can be used.
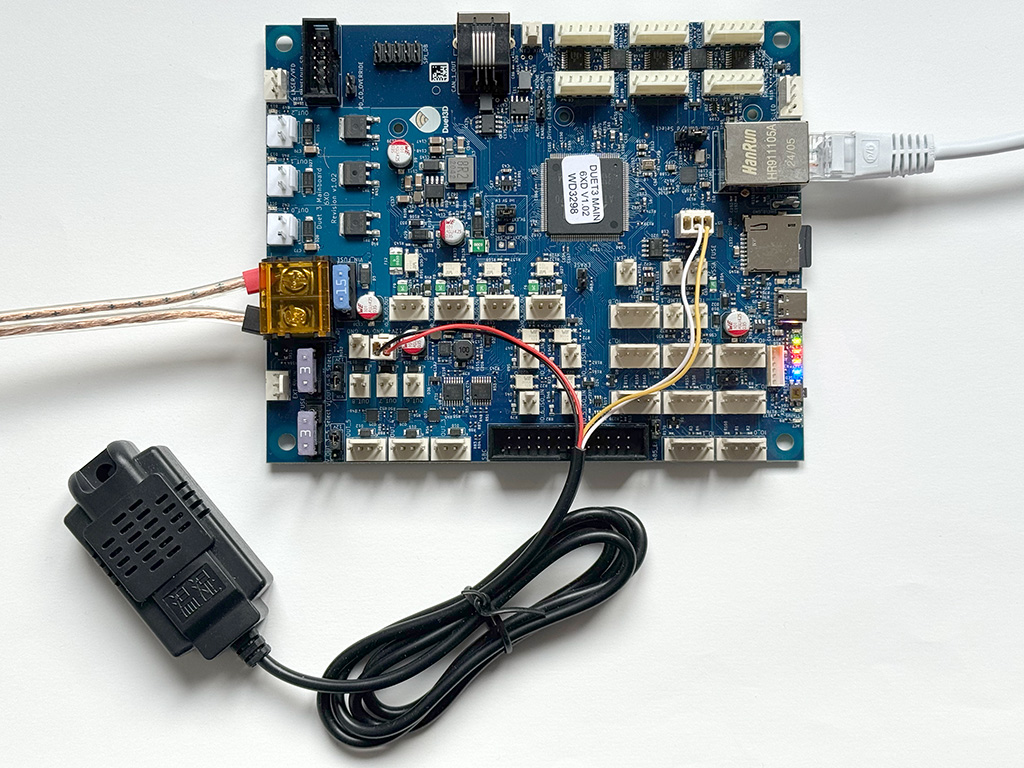
Image: A Duet 3 Mainboard 6XD v1.02 connected to a Modbus RTU temperature and humidity sensor, using the built-in RS485 adapter.
¶ What is RS485?
RS485 is a serial communication standard, and is one of the most widely used. It has a number of advantages over other standards that make it particularly suitable for noisy industrial areas.
- Long Communication Distances: devices can communicate with each other over a long distance (up to 1200m) using RS485 communication.
- High Data Rates: RS485 supports a wide range of data rates, from a few hundred bits per second to 10 mbit/s.
- Multidrop Configuration: RS485 supports multiple devices connected to the same communication bus. This enables the creation of complex networks with a single communication line.
- Robust Performance in Noisy Environments: RS485 uses differential signalling, where data is transmitted as the voltage difference between two lines, with voltage levels from -7V to +12V. This provides better noise immunity and reduces the impact of common-mode interference. Along with shielded and twisted pair cabling, this helps maintain reliable communication in the presence of interference.
- Cost-Effective Networking: Building RS485 networks is cost-effective, especially for applications where long distances and multiple devices need to be connected. The simplicity of the standard contributes to lower implementation costs.
- Wide Industry Adoption: RS485 has been widely adopted in industrial and building automation, HVAC systems, process control, and other applications. Its acceptance as an industry standard contributes to the availability of compatible devices and components.
¶ What is Modbus RTU?
Modbus RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) is a communications protocol in industrial automation, recognised for its simplicity and efficiency in allowing reliable communication between devices over serial connections such as RS485, and is widely supported.
Modbus RTU works on a master-slave architecture. Each Modbus message follows a structured format consisting of an address field, function code, data field, and checksum. The master initiates a request, specifying the starting address and required Modbus registers, while the slave responds with the requested data. The protocol supports both RTU communication (binary encoding for efficiency) and ASCII mode (human-readable but slower).
Note that the Duet mainboard is the master device, and can not be configured as a slave device.
Diving further into the specifics of the Modbus RTU protocol is beyond the scope of this documentation. There are many guides available, for example see Modbus RTU: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Implementing the Protocol
¶ Requirements
- Duet 3 Mainboard - 6HC, 6XD or Mini 5+ (Duet 2 not supported due to memory limitations)
- An RS485 adapter or transceiver.
- Duet 3 Mainboard 6HC v1.02c and later, and Duet 3 Mainboard 6XD v1.02 and later, have an RS485 adapter built-in.
- For other Duet 3 boards, RS485 transceivers are available cheaply from many online sellers. Look for one using MAX485 or MAX3485 chip. Most support automatic Tx/Rx switching, but some devices may not support this. There are also RS485 transceivers that have an extra input for firmware control of Tx/Rx switching, which you will need a spare pin to control. Jay from TeamGloomy did a round-up here: TeamGloomy github.io
- Wiring - see below
- An RS485 device, such as a sensor, relay, PLC or VFD, with its datasheet
¶ Hardware configuration
¶ Enabling the RS485 transceiver
Duet 3 Mainboard 6HC v1.02c and later, and Duet 3 Mainboard 6XD v1.02 and later, with an RS485 adapter built-in:
- These boards have hardware support for the MODBUS RTU from the RS485 header. This is shared with the IO1 GPIO channel so if used, do not connect endstops or anything else to the IO1 pins.
- Fit the RS485_EN jumper to enable the RS485 transceiver (see wiring diagrams for location)
For other Duet 3 boards with external RS485 transceivers
- Select an IO header on the Duet to use. This needs to be UART capable, and is usually either IO0 or IO1.
- Wire Duet io#.out to RS485 transceiver TX pin, and io#.in to RX pin. Wire VCC to voltage as appropriate (usually 3.3V or 5V) on the Duet, and GND to GND on the Duet.
- If using an RS485 transceiver that allows firmware control of Tx/Rx switching, wire the pin on the transceiver to a spare io#.out pin, e.g. io2.out.
¶ Wiring
¶ Wire specification
- For short cable runs to individual devices, generally the cable does not need to be twisted pair, shielded or have additional termination.
- For longer runs with the bus supporting multiple devices, twisted pair cable reduces interference, ideally with matching impedance (around 120 ohms). Choose an appropriate cable category (e.g. Cat 5e), consider shielding for high interference environments, and use termination resistors. Factor in distance, flexibility, and durability, ensuring compatibility with RS-485 connectors (e.g. DB-9, DB-25) for reliable performance.
¶ Wiring the device
- Wire the device to the RS485 header on the Duet or the RS485 transceiver.
- On 6HC and 6XD mainboards with built-in RS485 transceiver, the pins are 485_A and 485_B.
- On external RS485 transceivers, the pins may be marked A/+/A+/D+ and B/-/B-/D-.
- The device datasheet should say which wires should connect to which RS485 pin.
- Provide power to the device as necessary, either from an external PSU, or from the Duet.
¶ Wiring multiple devices
- Multiple devices can be wired in a daisy-chain or bus topology.
- Connect the A pin to the A pin of each subsequent device. Connect the B pin to the B pin of each subsequent device. Do not connect A to B, or B to A.
- Twisted pair cabling, shielding and termination may be required for longer runs.
- Ground any shielding at one end, ideally the Duet mainboard end.
¶ Firmware configuration
Configure the firmware to use the RS485 transceiver with M575, where:
- Pnnn: Serial channel number. Note that P0 = USB, P1 = io0, P2 = io1
- Bnnn: Baud rate, default 57600bps. Set this to match your device
- Snnn: serial port mode. 1 by default, set to 7 for 'Device' for Modbus
- C"port_name": Port name for firmware Transmit/Receive control of the RS485 transceiver.
Note: Not required when running on Duet hardware with a built-in RS485 transceiver. Not required if the transceiver module does automatic transmit/receive switching (note that such transceivers may not work with some Modbus devices).
Add one of the following examples to config.g:
- For Duet 3 boards with built-in RS485 transceivers, or mainboards using an external RS485 transceiver with automatic Tx/Rx switching:
M575 P2 B9600 S7 ; enable RS485 on serial channel 2 (io1), baud rate 9600bps, mode 7 (device/Modbus) - for mainboards using an external RS485 transceiver with firmware Tx/Rx switching:
M575 P2 B9600 S7 C"io1.out"; enable RS485 on serial channel 2 (io1), baud rate 9600bps, mode 7 (device/Modbus), using io1.out to control Tx/Rx switching
¶ Testing communications with device
¶ Gcode commands
The Modbus RTU implementation in RepRapFirmware uses Gcode to form the Modbus message, so knowledge of the underlying message structure is not generally necessary. You will need your device's documentation to know the device address (usually set to a default initially), the commands supported, and the registers, coils and/or inputs that need to be read or written to.
M261.1 - read data from a device
M260.1 - write data to a device
M260.4 - Raw Modbus transaction
¶ Gathering information on your device
To use the Gcodes, you will need some information on your Modbus RTU device. Generally, the best place for this is the device's datasheet.
In the following sections, an XY-MD01 environment sensor, which measures temperature and humidity, is used as an example. See the picture at the beginning of this page for the wiring setup. You will need to know the Modbus device address, the register you need to read or write to, the values to write, and the Modbus function codes. This is the useful information from the XY-MD01 sensor datasheet:
Product Name: Modbus RTU RS485 SHT20 Temperature Humidity Transmitter
Product Number: XY-MD01
Output signal:RS485 signal
Communication protocol:Modbus RTU and ordinary protocol
Communication address:1~247(default 1)
| Modbus Protocol | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Function Code | ||||
| Command Register | Function | |||
| 0x03 | Read keep register | |||
| 0x04 | Read input register | |||
| Ox06 | Write a single keep register | |||
| Ox10 | Write more keep registers | |||
| Register Type | Register Address | Register Contents | Bytes | |
| Input Register | 0x0001 | Temperature | 2 | |
| 0x0002 | Humidity | 2 | ||
| Keep Register | 0x0101 | Device Address | 2 | |
| 0x0102 | Baud Rate: 0:9600 1:14400 2:19200 |
2 | ||
| Ox0103 | Temperature Correction -10°C~10°C |
2 | ||
| 0x0104 | Humidity Correction -10%RH~10%RH |
2 | ||
Note the numbers for registers and contents are in hexadecimal, but the Gcode parameters are decimal, so some conversion is required.
¶ Read data from device
Use M261.1 to read data from a Modbus RTU device, where the parameters are:
- Pnn Port to request data through, same numbering as in M575 command (1 = first aux port, 2 = second aux port). The port must already have been put into Device mode using M575.
- Ann Modbus device address
- Rnn Register number to start from
- Bnn How many registers,coils or inputs to request
- Fn (optional) Modbus function code, must be one of: 1 (Read Coils), 2 (Read Discrete Inputs), 3 (Read Holding Registers), 4 (Read Input Registers, default)
- V"name" (optional) name of a new variable to receive data into. If this parameter is not present then the data read is output to the console.
Sending a correctly formed M261.1 command like the following example from the console will receive the data as hexadecimal:
M261.1 P2 A1 R1 B2 F4
Received 00de 0228
This is the temperature and pressure reading from an XY-MD01 sensor. 00de = 222 in decimal, which is divided by 10 to get 22.2°C. 0228 = 552 decimal, which is 55.2% humidity.
From holding/keep registers (ie device settings), where the first register is 0x0101 hex = 257 decimal:
M261.1 P2 A1 R257 B1 F3 ; register for device address
Received 0001
M261.1 P2 A1 R258 B1 F3 : register for device baud rate (2580 hex = 9600bps)
Received 2580
M261.1 P2 A1 R259 B1 F3 : register for temperature correction
Received 0000
M261.1 P2 A1 R260 B1 F3 : register for humidity correction
Received 0000
Or to retrieve all of them at once:
M261.1 P2 A1 R257 B4 F3
Received 0001 2580 0000 0000
¶ Write data to device
Use M260.1 to write data to a Modbus RTU device, where the parameters are:
- Pnn Serial port to send/receive through, numbered as in M575 (1 = first aux port, 2 = second aux port). The port must already have been set to Device mode using M575.
- Ann Modbus slave device address
- Fn (optional) Modbus function code, must be one of: 5 (Write Single Coil), 6 (Write Single Register), 15 (Write Multiple Coils), 16 (Write Multiple Registers, default)
- Rnn First Modbus coil or register number to write to
- Bnn:nn:nn... One value per coil or register to write. If writing registers, each value is a 16-bit word to write. If writing coils, each value is zero to set coil off, nonzero to set coil on.
- S"ascii data" data to send (alternative to B parameter). Each character is converted to the corresponding ASCII value. Ignored if B parameter is present.
For example, changing the device address, where the register is 0x0101 hex = 257 decimal:
M260.1 P2 A1 F6 R257 B3
(cycled power)
M261.1 P2 A3 R1 B2 F4
Received 00df 022f
¶ Raw Modbus transaction
Sometimes a Modbus device may not adhere strictly to the Modbus RTU protocol, or have additional functions or settings that can be accessed by sending special commands. The device datasheet should outline what the device expects, and RepRapFirmware can send these commands using M260.4.
As an example, the datasheet of the XY-MD01 environment sensor shows the following format is required to retrieve the temperature:
| Master Read Temperature Command Frame (0x04) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Device Address |
Function Code |
Starting Address Hi |
Starting Address Li |
Quantity Hi | Quantity Li | CRC Hi | CRC Li |
| 0x01 | 0x04 | 0x00 | 0x01 | 0x00 | 0x01 | 0x60 | 0x0A |
| Response Temperature Value from Slave | |||||||
| Device Address |
Function Code |
Bytes | Temp Hi | Temp Li | CRC Hi | CRC Li | |
| 0x01 | 0x04 | 0x02 | 0x01 | 0x31 | 0x79 | 0x74 | |
From this, you can create the Modbus command using M260.4. The parameters are:
- Pnn Serial port to send/receive through, numbered as in M575 (1 = first aux port, 2 = second aux port). The port must already have been set to Device mode using M575.
- Ann Modbus slave device address
- Rnn Number of bytes to receive excluding the slave address and the CRC
- Bnn:nn:nn... Values to send excluding the slave address and the CRC
- S"ascii data" data to send (alternative to B parameter). Each character is converted to the corresponding ASCII value. Ignored if B parameter is present.
- V"name" (optional) name of a new variable to receive data into. If this parameter is not present then the data read is output to the console.
RepRapFirmware will still need the serial port (P parameter) and Modbus device address (A parameter), and will calculate the CRC for you. It will also need to know how many bytes to return from the response (R parameter). Then the B parameter holds the values in hex you want to send, in this example the function code, two bytes for the address, and two bytes for the number of registers to return.
M260.4 P2 A1 B{0x04, 0x00, 0x01, 0x00, 0x01} R4
Received 04 02 00 dd
In this example, after the device address and CRC are checked and removed, we received back the function code, the number of bytes returned, and the two bytes for the temperature.
¶ Using data from devices
Generally, you will want to use the data retrieved from the Modbus RTU connected device. RepRapFirmware provides the M261.1 V parameter to read the data into a variable. Note that:
- If the V parameter is not present, then the data read is output to the console in hexadecimal.
- The variable created by the V parameter is an array, even if only one register/coil is read.
- The variable created by the V parameter only exists within the scope (the scope of a local variable is the remainder of the block in which it is declared), so you will need to assign the value to a global variable if you want to use the value outside of the scope or macro.
- Data returned by the V parameter is converted from hexadecimal to decimal.
- Typically, the data returned from Modbus is one or more registers and the data may need to be converted or scaled.
For example, to use the temperature and humidity values returned by a Modbus sensor, first declare a couple of global variables (in config.g):
global temperature = 0
global humidity = 0
Then create a macro which reads the data from the sensor, and sets the global variables. Note that the variable 'modbusResult' only exists within the scope of the macro:
M261.1 P2 A1 R1 B2 F4 V"modbusResult"
set global.temperature = var.modbusResult[0]/10
set global.humidity = var.modbusResult[1]/10
echo global.temperature ^ "°C, " ^ global.humidity ^ "%RH"
Result:
M98 P"0:/macros/Modbus read.g"
21.40000°C, 58.10000%RH
The values can be accessed by the object model, and used by other processes.
¶ Support for other Modbus devices
This section will be added to as more Modbus devices are connected to Duet mainboards and RRF.
¶ Environmental sensors
See the example above.
¶ Programmable Logic Controllers
Examples on the Duet3D forum:
Duet 6XD to a Productivity P1-550 PLC.
Duet 6XD to a Mitsubishi FX3u-485ADP-MB PLC with RS485 Adapter, with 60+ SMT PnP Electric Feeders connected to it. See towards the end of the thread.
Duet 6HC with external RS485 transceiver to a Beckhoff CX7080 PLC
¶ Variable Frequency Drives and spindles
Millennium Machines and user @NineMile have made great strides in getting VFDs to talk to RRF via RS485 and Modbus. They have created a "daemon macro framework for RepRapFirmware v3.6+, which helps to implement RS485 Spindle Control, Monitoring and Feedback across different VFD types." See the ArborCTL github repository here for details.
Currently supported VFDs (as of October 2025) are the Shihlin SL3, Huanyang HY02D223B and Yalang YL620A, with untested support of Huanyang GT-2R2G-2.