¶ Introduction
This document is relevant to: Duet 3 Mainboard 6HC, Mainboard 6XD and Mini 5+.
Firmware versions: All versions
Difficulty: Moderate
Time Required: 30 minutes - 1 hour
This guide covers connecting hardware, such as power, heaters, motors, endstops, fans, temperature sensors etc., to your Duet 3 mainboard.
If you are setting up your Duet 3 with a connected Single Board Computer (SBC, eg Raspberry Pi), please see SBC setup for Duet 3 documentation for connecting the SBC.
If you have any problems with your Duet when using this guide, rather than posting comments, please use our support forum: https://forum.duet3d.com/
¶ 1. Board Diagram
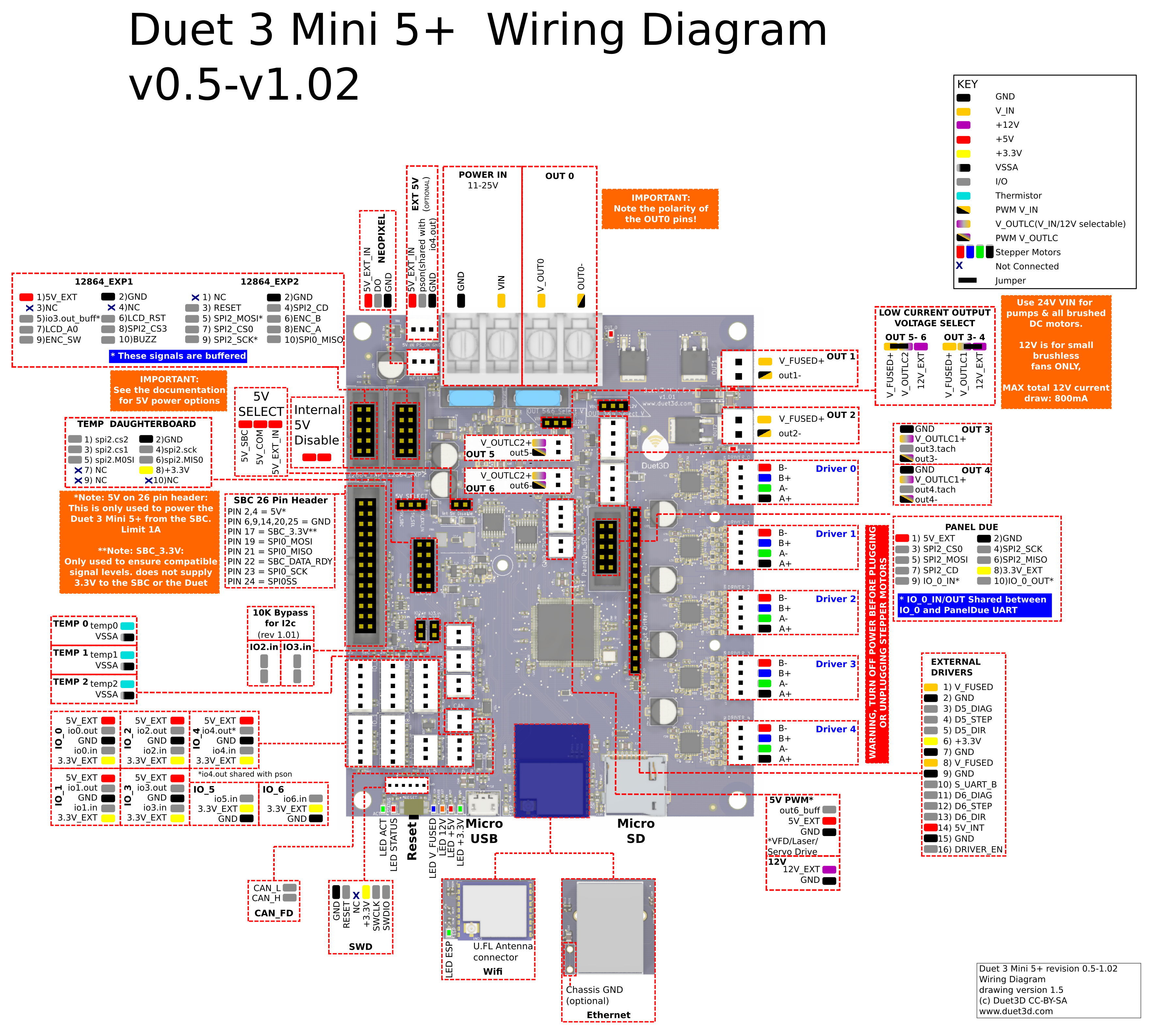
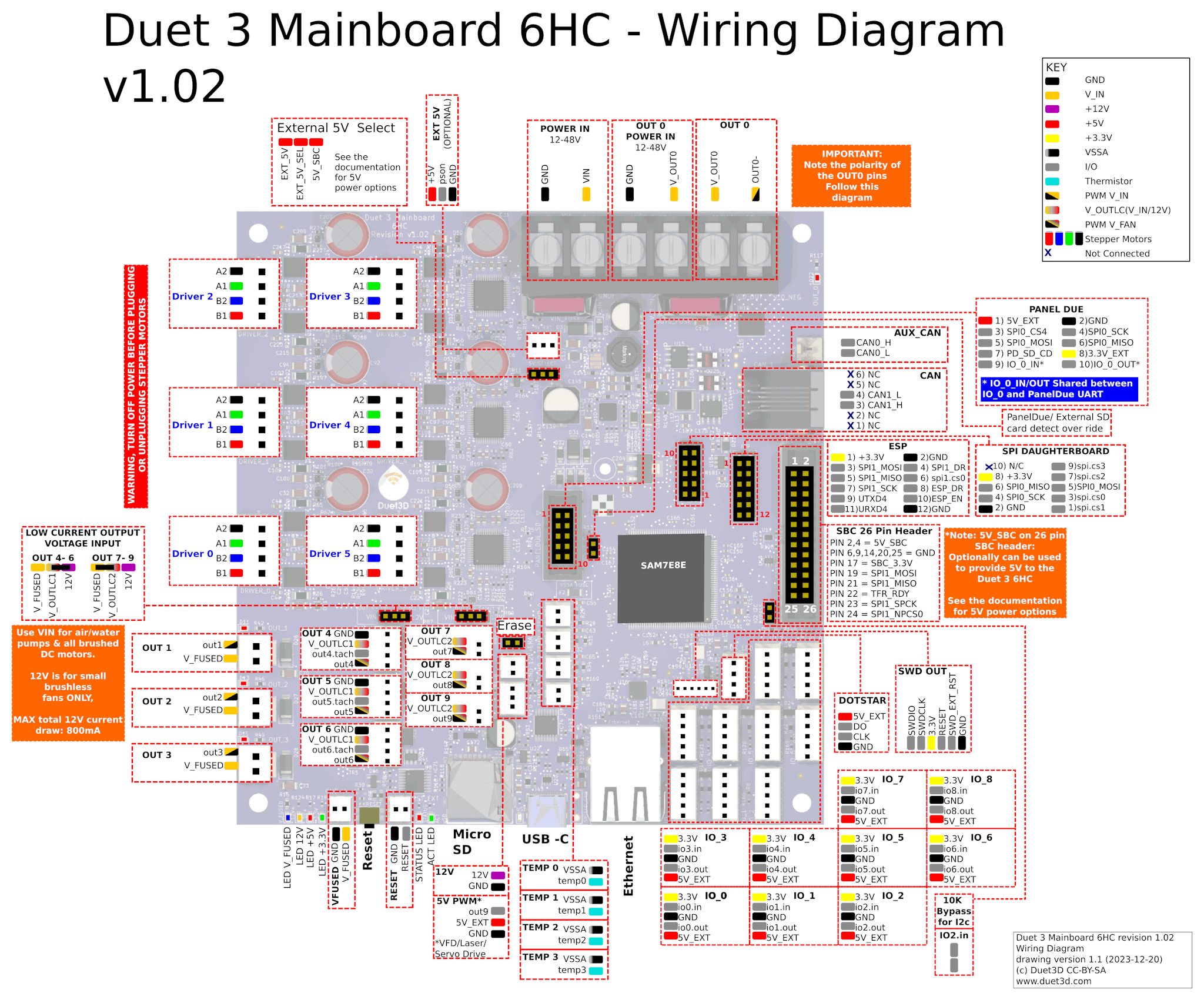
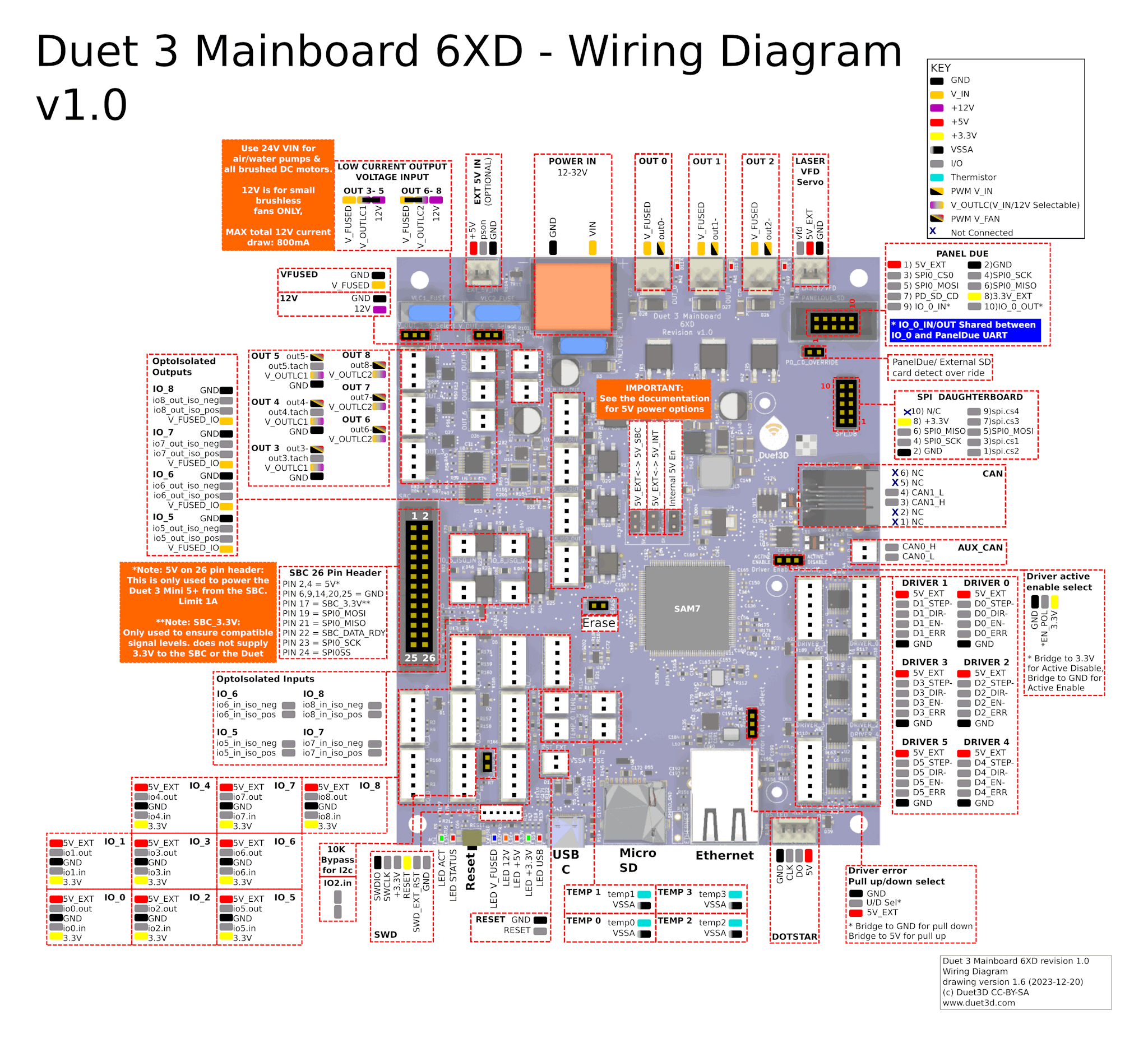
Take a moment to familiarise yourself with the wiring diagram. Click on the image to open the full resolution version in a new browser window/tab.
For wiring diagrams of older board versions, see Duet 3 Mini 5+ hardware overview.
For wiring diagrams of older board versions, see Duet 3 Mainboard 6HC hardware overview.
For wiring diagrams of older board versions, see Duet 3 Mainboard 6XD hardware overview.
¶ 2. Fire safety
WARNING: it is HIGHLY recommended that you use the provided crimped connectors for the power supply, bed heater and hotend heaters.
- Failure to use these can result in wire creeping, causing the wires to come loose in the screw terminal and possibly create a hot spot or short circuit, which could result in fire.
- Using bare wires may lead to stray wire strands causing short circuits, which could result in fire.
- Do not tin (add solder to) these wires. The solder will flow over time, and will become loose in the screw terminal and possibly create a hot spot or short circuit, which could result in fire.
- The crimp tools shown below are generally available from any hardware store, electrical shop, online etc., and when used correctly will give good quality, solid connections.
- The method of crimp used is called an indent crimp. You should ensure that the tool you use provides a tight crimp of the ferrule to the wire.
- It is also best to use the included Molex connectors for all other connections as they ensure correct polarity and lock into place.
¶ 3. Tools required
To complete the wiring of your Duet, you will usually need:
- Screwdrivers (flat blade and Pozidriv)
- Wire stripper/cutter
- Crimping tool(s) (see tabs below)
- Pliers
¶ Crimping the connectors
Here is a good guide to crimping: Teaching Tech on YouTube

 Duet 3 mainboards have a barrier strip with screw terminals to connect power supply wires, and are supplied with insulated spade crimps.
Duet 3 mainboards have a barrier strip with screw terminals to connect power supply wires, and are supplied with insulated spade crimps.
- Duet 3 Mainboard 6HC uses a 6-way barrier strip for Power in (VIN), OUT0 power in, OUT0 (high current output, eg heated bed, max 15A, can be different voltage than main power in.)
- Duet 3 Mini 5+ uses a 4-way barrier strip for Power in (VIN), OUT0 (high current output, eg heated bed, max 15A).
- Duet 3 Mainboard 6XD uses a 2-way barrier strip for Power in (VIN).
Standard red/blue/yellow automotive crimp tools will crimp these terminals. There are ratchet tools to crimp these as well as low-cost non-ratchet tools; we find ratchet wire crimping tools produce better crimps than the non-ratcheting type.

 Duet 3 mainboards use JST-VH series connectors for medium current outputs:
Duet 3 mainboards use JST-VH series connectors for medium current outputs:
- Duet 3 Mainboard 6HC: used for the 4-wire motor outputs (Driver 0 to 5) and OUT1, OUT2 and OUT3
- Duet 3 Mini 5+: used for OUT1 and OUT2
- Duet 3 Mainboard 6XD: used for OUT0, OUT1 and OUT2
JST-VH crimps require a minimum of 22AWG wire (20AWG or 0.5mm2 recommended. Most NEMA17 size stepper motor wire will will not be thick enough to use in the normal way, but you can double the stripped part of the wire back on itself to bulk it up, and put a small length of heat shrink sleeving over the insulation to bulk up the insulation.
You will need a suitable crimping tool for the crimp pins, for example Engineer PA21. The PA21 is designed to handle the longer flanges of the VH crimps that grip the insulation. Use the 2.2mm jaw opening to crimp the bare wire and the 2.5mm on to crimp the insulation. The large side of a ratchet crimping tool, such as the HT-225D, may also be able to crimp the VH series. The Iwiss SN-2549 ratchet cripping tool claims to be compatible with JST VH crimp pins and all other pin connectors currently use by Duets.

 Molex KK-compatible connectors are used for all other inputs and outputs on Duet mainboards. Use a manual tool such as Engineer PA-09/PA-20/PA-21 (use the 1.6mm opening for the bare wire, and 1.9mm opening for the insulation), or ratchet crimping tool, eg HT-225D ratchet crimper. The Iwiss SN-2549 ratchet cripping tool claims to be compatible with Molex crimp pins and all other pin connectors currently use by Duets.
Molex KK-compatible connectors are used for all other inputs and outputs on Duet mainboards. Use a manual tool such as Engineer PA-09/PA-20/PA-21 (use the 1.6mm opening for the bare wire, and 1.9mm opening for the insulation), or ratchet crimping tool, eg HT-225D ratchet crimper. The Iwiss SN-2549 ratchet cripping tool claims to be compatible with Molex crimp pins and all other pin connectors currently use by Duets.
 Most Duet 3 expansion boards use the same connectors as the main boards. The exception to this is the Duet 3 Toolboard 1LC, which uses JST-PH and JST-ZH connectors to keep the size of the board as small as possible.
Most Duet 3 expansion boards use the same connectors as the main boards. The exception to this is the Duet 3 Toolboard 1LC, which uses JST-PH and JST-ZH connectors to keep the size of the board as small as possible.
The JST-PH connectors can be crimped using a manual tool such as Engineer PA-09, or pre-crimped connectors are available from electrical retailers. The Iwiss SN-2549 ratchet cripping tool claims to be compatible with JST PH crimp pins and all other pin connectors currently use by Duets except JST ZH.
The JST-ZH connectors (used for CAN and 1LC v1.0 headers) are difficult to crimp because they are so small, so Duet3D supply pre-terminated connectors. You can connect longer wires to them by hand soldering or using small size (white) solder sleeves. They can be manually crimped with Engineer PA-09, good eyesight and a steady hand.
¶ 4. Communicating with the Duet board
- You should begin by checking the Duet board and get it connected to your network. Please refer to Getting Connected to Your Duet for details.
- Once you have established communication, unplug the USB lead.
- All wiring should be done with NO POWER to the Duet board!
¶ 5. LED Indicators
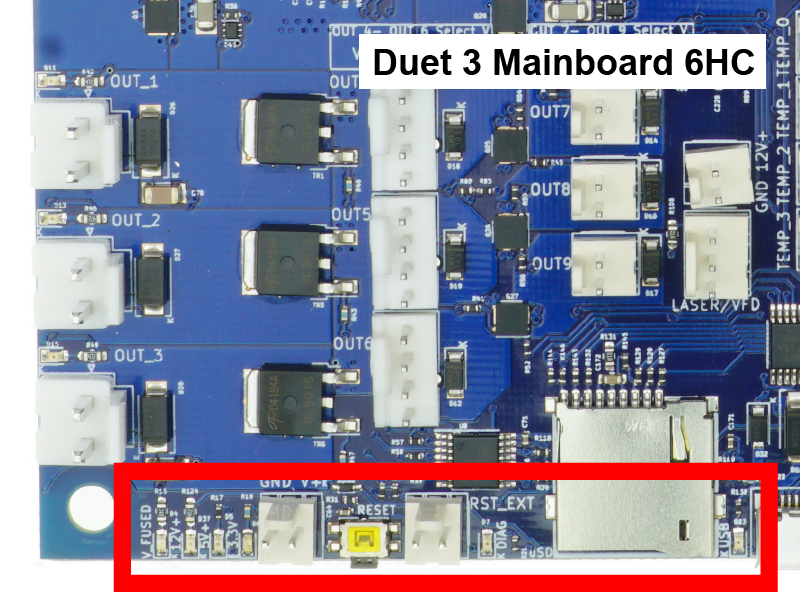
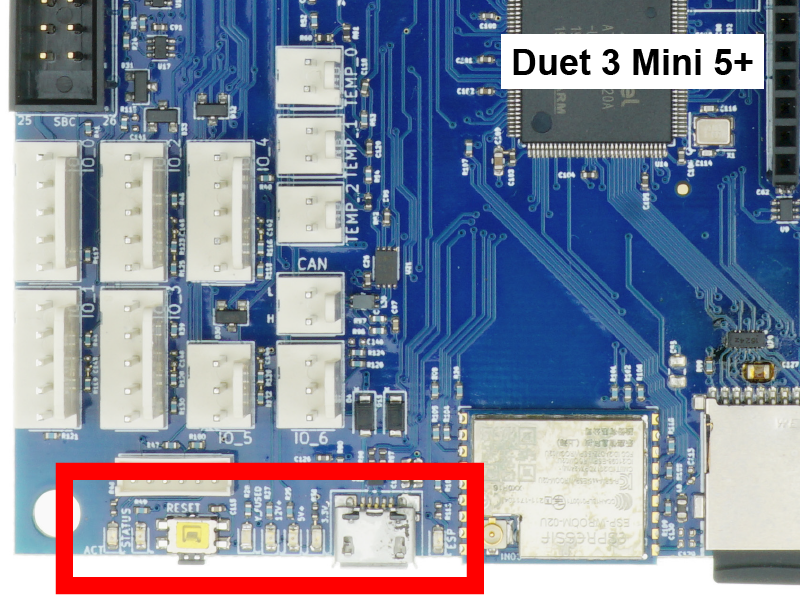 On the edge of the board around the reset button are a number of LEDs.
On the edge of the board around the reset button are a number of LEDs.
- These indicators show the status of 3.3V power, 5V power, 12V power and Vin (power from your power supply).
- When the board is idle and connected to a power supply, expect the 3.3v, 5v, 12v and Vin LEDs to be illuminated, and the STATUS/DIAG LED to be flashing steadily.
- When the board is powered only through an external 5v supply or through USB, expect only the 5v and 3.3v lights to be on.
- There are also LED indicators on the board to show when each high current OUT_x outputs are turned on.
The LED indicators have the following function:
| Label | Colour | Function |
|---|---|---|
| ACT | Green | Indicates activity on the CAN-FD bus (Mini 5+, 6XD) |
| STATUS/DIAG | Red | See description below |
| V_FUSED | Blue | Indicates fused VIN supply present |
| 12V+ | Amber | Indicates indicates on-board 12V regulator operating |
| 5V+ | Red | Indicates indicates 5V supply present |
| 3.3V+ | Green | Indicates on-board 3.3V regulator operating |
| USB | Red | Indicates presence of 5V power from USB (6HC) |
| ESP | Green | Indicates WiFi activity; flashing for searching/connecting, on for connected. (Mini 5+ WiFi version) |
The red LED labelled "STATUS" (Mini 5+, 6XD) or "DIAG" (6HC) indicates the state of the board, as follows.
| LED | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Flashing steadily, about half a second off and half a second on | Normal operation, RepRapFirmware is running |
| Glowing dimly, or off | Firmware has been erased (6HC, 6XD) |
| Pulsing from bright to dim and back again | USB bootloader activated (Mini 5+) |
| Flashing three times, then off for a while | Firmware CRC check failed |
¶ 6. Powering the Duet board
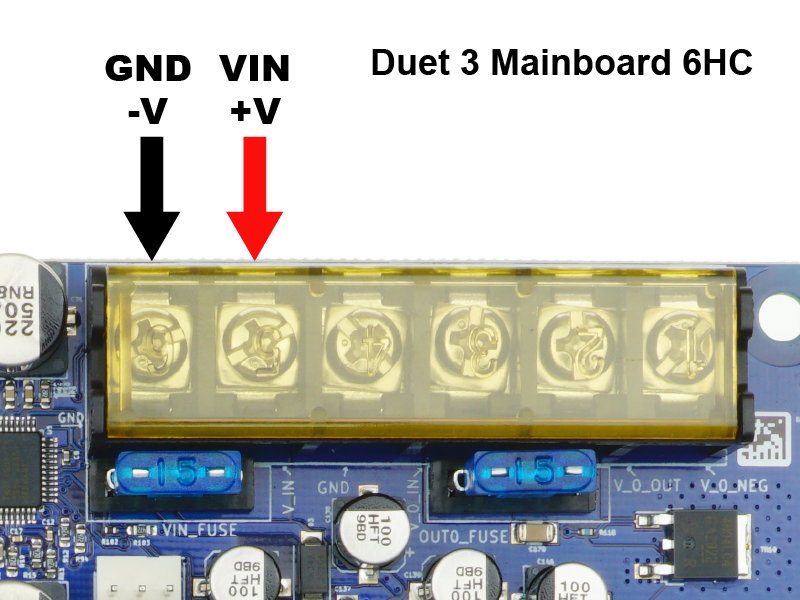
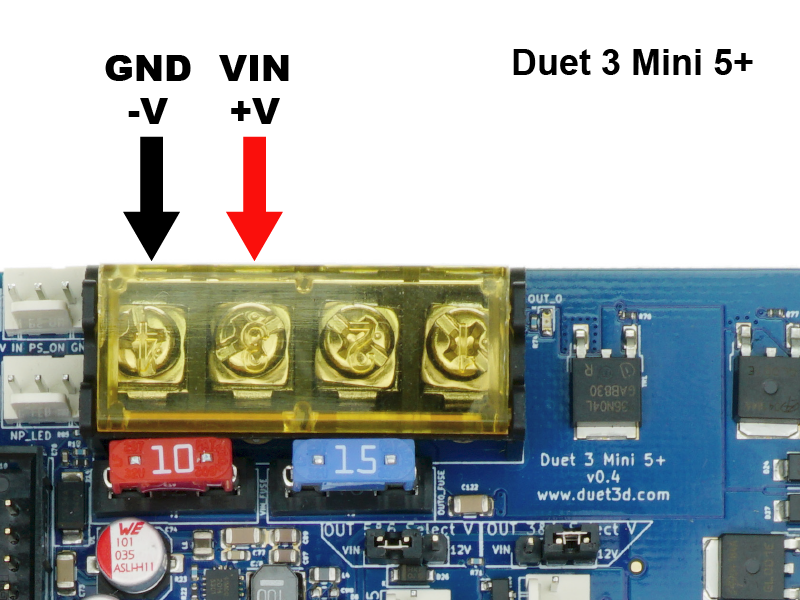 Connect your power supply wires to the Power In screw terminals of the barrier strip.
Connect your power supply wires to the Power In screw terminals of the barrier strip.
- Be sure to observe correct polarity when making the connections.
- WARNING: It is HIGHLY recommended to use the included fork terminals, by crimping them to the wires before putting the wires in the terminal block. Failure to do so could allow the wires to creep over time, become loose, and could possibly short circuit and start a fire.
- Do not tin (add solder to) these wires. The solder will flow over time, and will become loose in the screw terminal.
- Be sure not to twist the barrier strip while tightening the screws. It can help to hold the barrier strip while tightening.
- Check the screws after a few days/week of operation to ensure they are still snug.
- The gauge of wire should be appropriate to the current that the Duet will draw. This depends on a number of factors, however at its maximum this will be dominated by the 15A for the bed heater. The fork terminals supplied with Duet 3 boards are suitable for wire 1.5mm² to 2.5mm², 16 AWG to 14 AWG.
- Once connected, make sure USB is disconnected (no power to board). Test the power by turning it on. You should see the LEDs on the edge of the board light up, with the 3.3v, 5v, and Vin LEDs illuminated.
- TURN OFF THE POWER SUPPLY. All wiring should be done with no power to the Duet board.
- For more details, see User manual: Choosing the power supply and User manual: Power wiring
¶ 7. Reset button and firmware erase
¶ Reset button
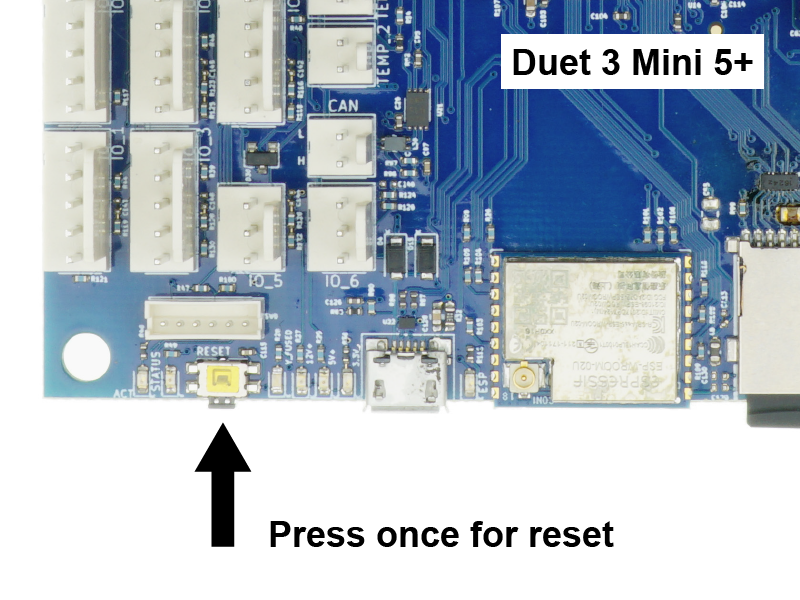
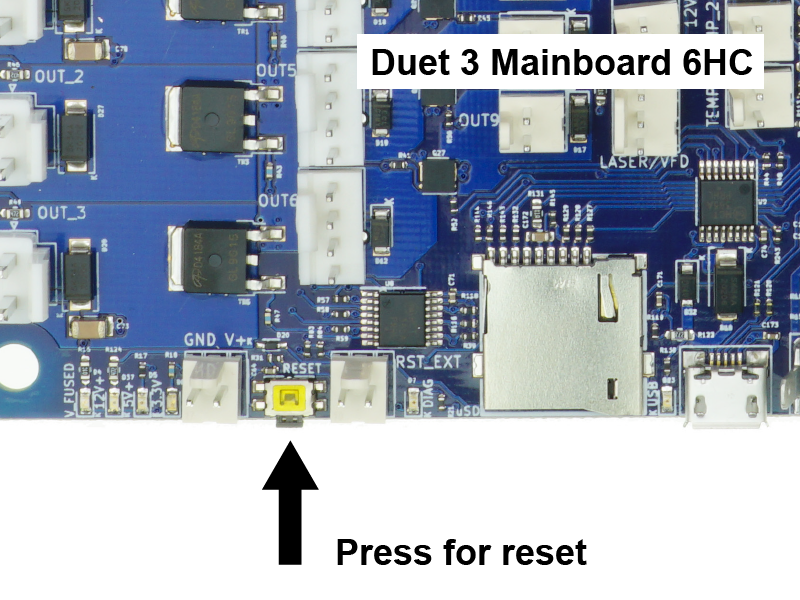 The reset button reboots the board. Press if a reboot is needed.
The reset button reboots the board. Press if a reboot is needed.
¶ Firmware erase
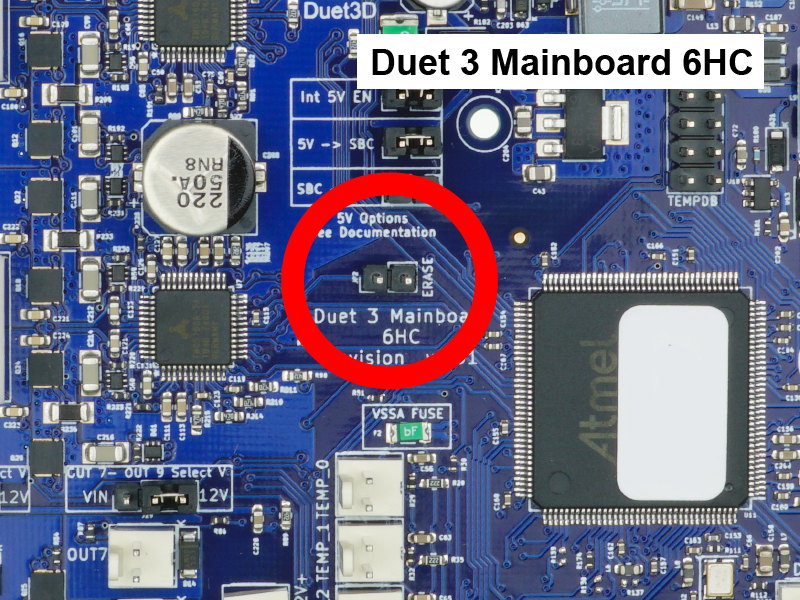
 Do not erase the firmware unless you know what you are doing. The firmware does not need to be erased for normal updating. The process of reinstalling the firmware after it is erased is detailed here: User manual: Updating firmware.
Do not erase the firmware unless you know what you are doing. The firmware does not need to be erased for normal updating. The process of reinstalling the firmware after it is erased is detailed here: User manual: Updating firmware.
6HC, 6XD:
- Bridge the 'Erase' pins with a jumper, and apply power, to erase the firmware. Remove the jumper before flashing firmware.
- The erase jumper will erase the firmware that is stored on the main processor. The SD card does not hold the firmware, just the configuration files.
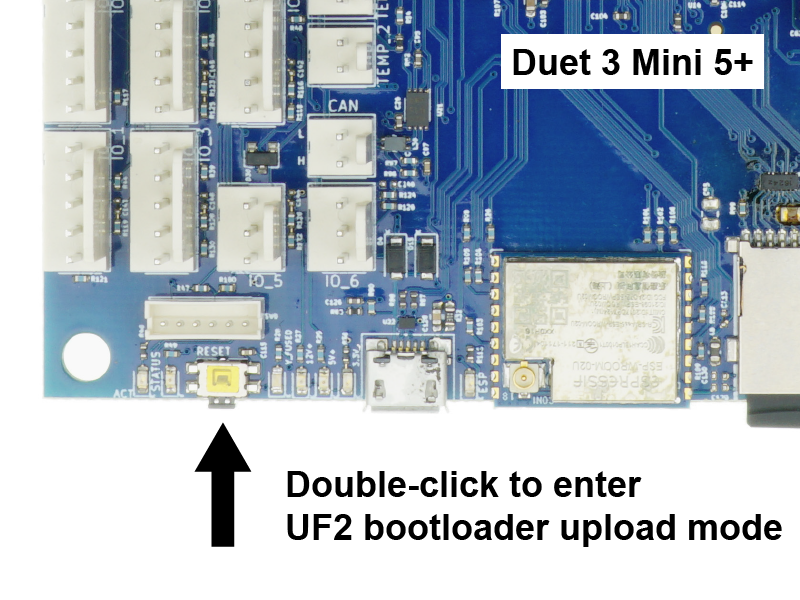
Mini 5+:
- There is no jumper or button to erase the firmware. However, a double press on the reset button will put the board into UF2 bootloader upload mode. See User manual: Updating firmware - Duet 3 Mini 5+ via USB
¶ 8. Endstops
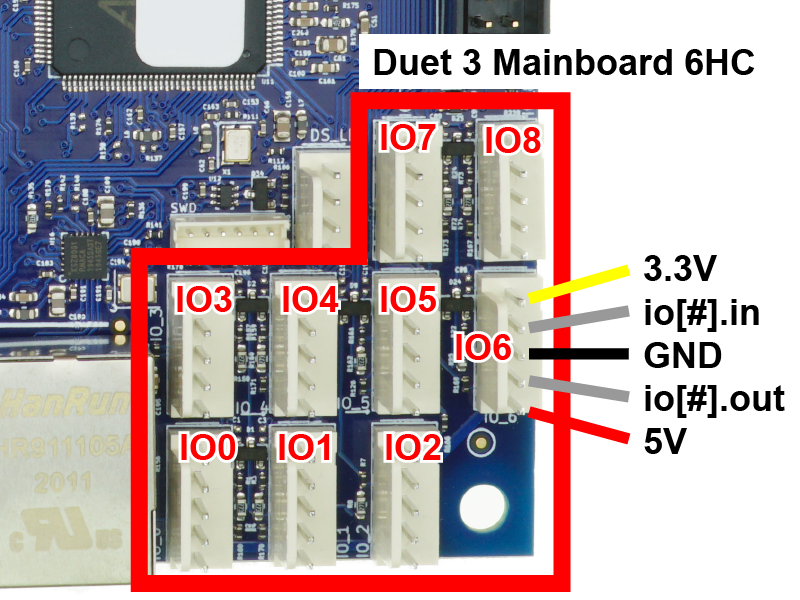
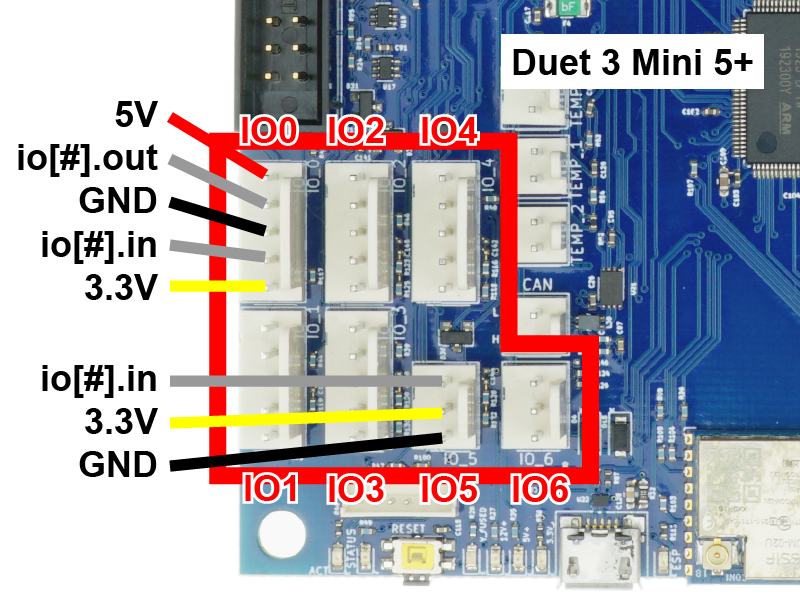 Endstops tell the printer when the travel limit has been reached on a particular axis. The Duet's connections may be different from other controller boards, so please review this step and your endstops carefully.
Endstops tell the printer when the travel limit has been reached on a particular axis. The Duet's connections may be different from other controller boards, so please review this step and your endstops carefully.
- You can connect simple microswitch endstops to any of the IO connectors.
- On an IO connector, the pins are +3.3V, signal in (labelled io[#].in), GND, signal out (labelled io[#].out) and +5V.
- Duet 3 Mini 5+: two of the IO connectors (IO5, IO6) are input only, with three pins. The pins are signal in (labelled io[#].in), +3.3V, and GND.
- If using 2-wire microswitch endstops, connect one wire to GND and the other wire to signal in.
- WARNING: Never connect your endstop wires from +3.3V or +5V to ground. This will create a short circuit and could damage the Duet.
- If using other endstops, please refer to User manual: Connecting endstop switches for details.
¶ 9. Z Probe
- Connect a probe to an appropriate IO connector (see above). You can have multiple probes, if necessary.
- There are many different kinds of probe, and the wiring will be different for each one.
- Some probes may need specific capabilities, e.g. analogue input or PWM output, that may only be supported by specific IO connectors; see the hardware overview for your board for IO connector capabilities.
- See User manual: Choosing a Z probe, which will help you choose a suitable Z probe if you have not already.
- See User manual: Connecting a Z probe, which contains guidance for wiring your Z probe to the Duet.
¶ 10. Fans
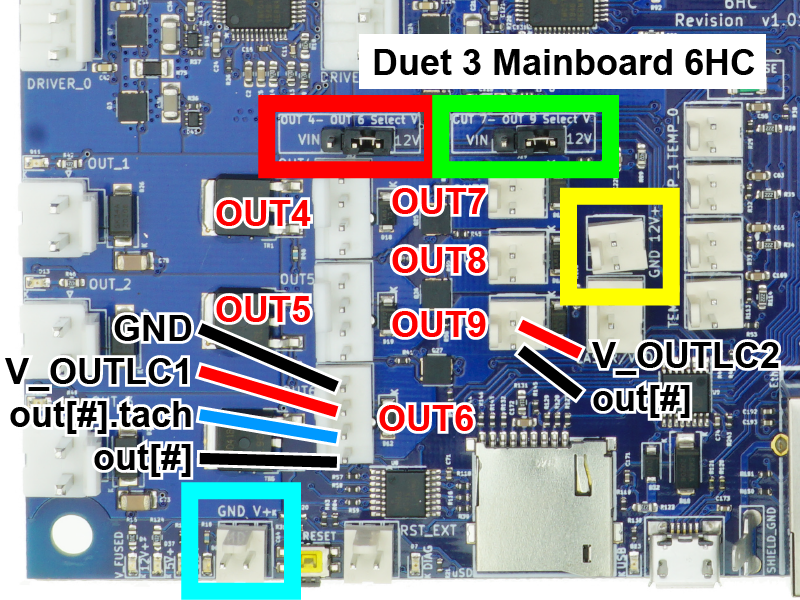
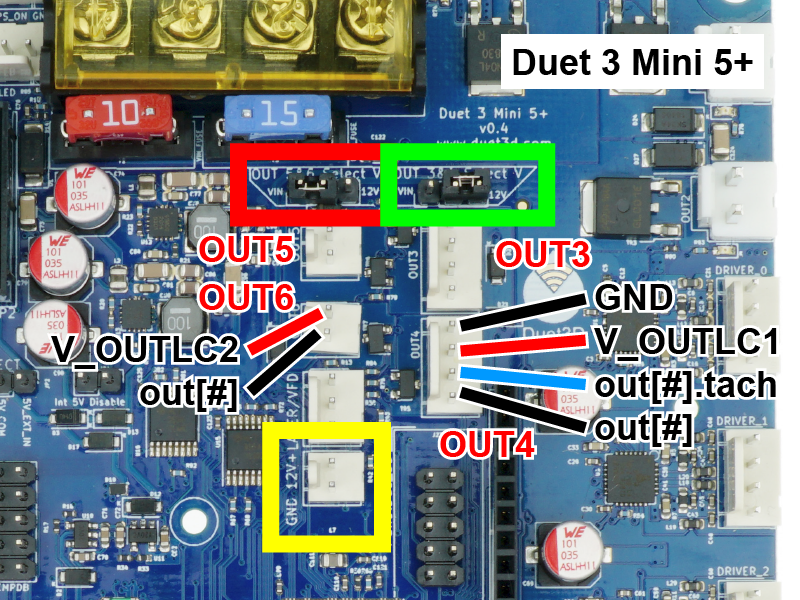
- The 6HC provides:
- 3 x 4-wire PWM-controlled outputs with tacho input: OUT4, OUT5 and OUT6.
Voltage is selectable between VIN / 12V / external power (provide required voltage to centre pin), using the OUT4-OUT6 Select V jumper. - 3 x 2-wire PWM-controlled outputs: OUT7, OUT8 and OUT9.
Voltage is selectable between VIN / 12V / external power (provide required voltage to centre pin), using the OUT7-OUT9 Select V jumper. - 1 x VIN-voltage, always-on output
- 1 x 12V, always-on output
- 3 x 4-wire PWM-controlled outputs with tacho input: OUT4, OUT5 and OUT6.
- A PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) fan connection is for fans you wish to control the speed of, for example a print cooling fan.
- An always on fan is for something like an electronics fan - always on when the printer is on.
- Some fans are more compatible with PWM control than others. If you have trouble varying the speed of a fan, check the documentation for changing PWM frequency.
- The polarity of the fans is important - don't connect them backwards, or you may damage the Duet board.
- When using the onboard 12V regulator (i.e. 12V has been selected and/or using 12V always on output), the TOTAL 12V current draw must not exceed 800mA.
- For more details, see User manual: Connecting and configuring fans
- The Mini 5+ provides:
- 2 x 4-wire PWM-controlled outputs with tacho input: OUT3 and OUT4.
Voltage is selectable between VIN / 12V / external power (provide required voltage to centre pin), using the OUT3&4 Select V jumper. - 3 x 2-wire PWM-controlled outputs: OUT5 and OUT6.
Voltage is selectable between VIN / 12V / external power (provide required voltage to centre pin), using the OUT5&6 Select V jumper. - 1 x 12V, always-on output
- 2 x 4-wire PWM-controlled outputs with tacho input: OUT3 and OUT4.
- A PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) fan connection is for fans you wish to control the speed of, for example a print cooling fan.
- An always on fan is for something like an electronics fan - always on when the printer is on.
- Some fans are more compatible with PWM control than others. If you have trouble varying the speed of a fan, check the documentation for changing PWM frequency.
- The polarity of the fans is important - don't connect them backwards, or you may damage the Duet board.
- When using the onboard 12V regulator (i.e. 12V has been selected and/or using 12V always on output), the TOTAL 12V current draw must not exceed 800mA.
- For more details, see User manual: Connecting and configuring fans
¶ 11. Temperature sensors
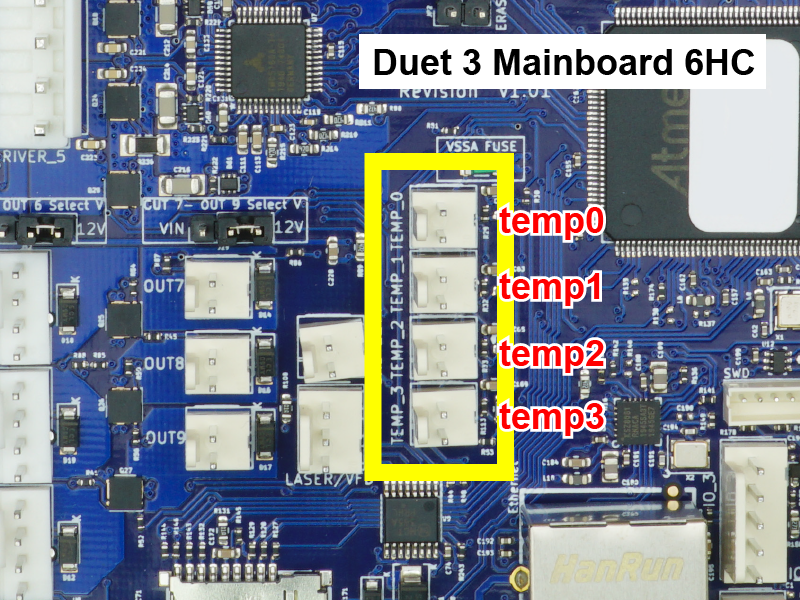
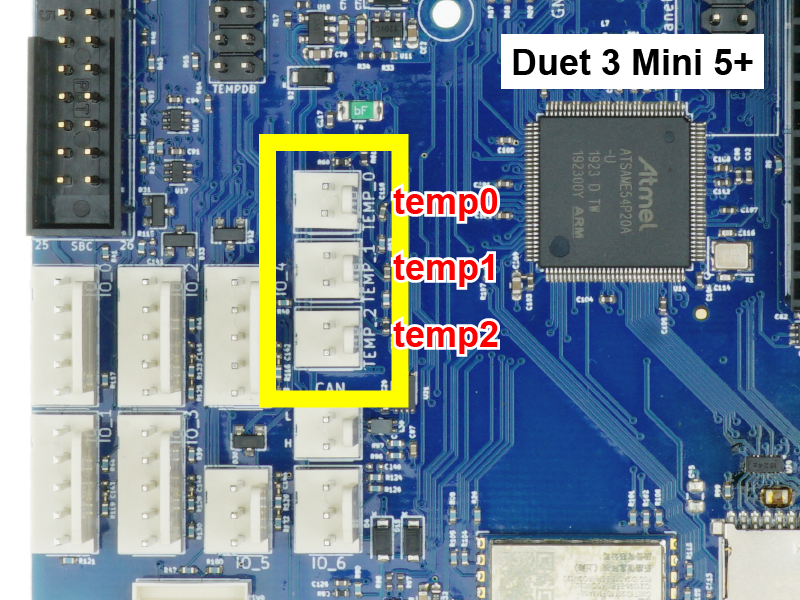 Duet 3 boards support thermistors and PT1000 temperature sensors, directly connected to the 'TEMP' headers on the board.
Duet 3 boards support thermistors and PT1000 temperature sensors, directly connected to the 'TEMP' headers on the board.
- The Duet 3 Mainboard 6HC and Duet 3 Mainboard 6XD support four temperature inputs. The Duet 3 Mini 5+ has three temperature inputs.
- Connect the thermistor/PT1000 to one of the temperature inputs.
- The polarity of the thermistor/PT1000 does not matter.
- It generally doesn't matter which temperature sensor you connect where, so long as you know which is which. You can configure any temperature input to any heater. However, it can help to organise them logically, for example connect the temperature sensor for heater0/out0 to temp0, for heater1/out1 to temp1, etc.
- Duet boards also support thermocouple or PT100 temperature sensors, using a temperature daughterboard (see Temperature Daughterboard step below).
- For choosing a temperature sensor appropriate for you application, see User manual: Choosing temperature sensors.
- For more details, see User manual: Connecting thermistors and PT1000 temperature sensors.
¶ 12. Bed Heater
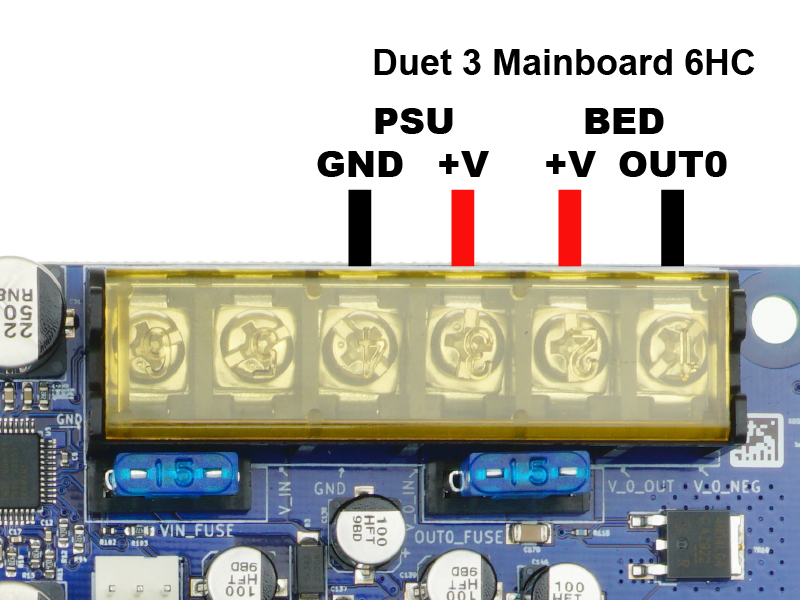
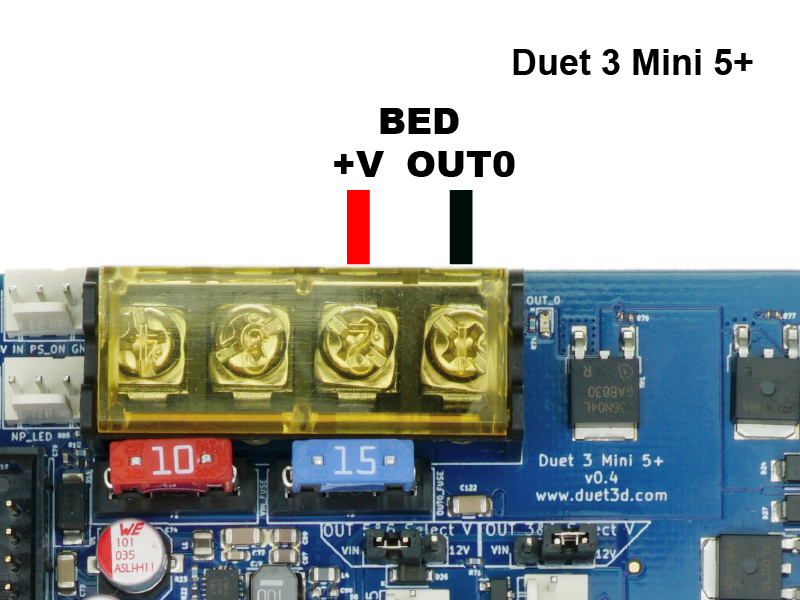 The Duet is able to power a heated bed, and is fused at 15A. This should be well above the requirement for most heated beds.
The Duet is able to power a heated bed, and is fused at 15A. This should be well above the requirement for most heated beds.
- Connect the heated bed to the OUT0 terminals of the Duet.
- Duet 3 Mainboard 6HC: provide power to the OUT0 POWER IN terminals.
- If your heater has an integrated LED, then the polarity will matter as the LED will not light with reverse polarity. Otherwise, a heater's polarity doesn't matter.
- WARNING: It is HIGHLY recommended to use the included fork terminals, by crimping them to the wires before putting the wires in the terminal block. Failure to do so could allow the wires to creep over time, become loose, and could possibly short circuit and start a fire.
- Do not tin (add solder to) these wires.
- Be sure not to twist the terminal block while tightening the screws. It can help to hold the terminal block while tightening.
- Check the screws after a few days/weeks of operation to ensure they are still snug.
- If you have a heated bed that draws more than 15A, or a mains-powered heated bed, this should not be connected directly to the Duet. It will be controlled using a Solid State Relay, which the Duet can be configure to turn on and off.
- For more details, see User manual: Connecting and configuring a bed heater.
¶ 13. Hotend heaters
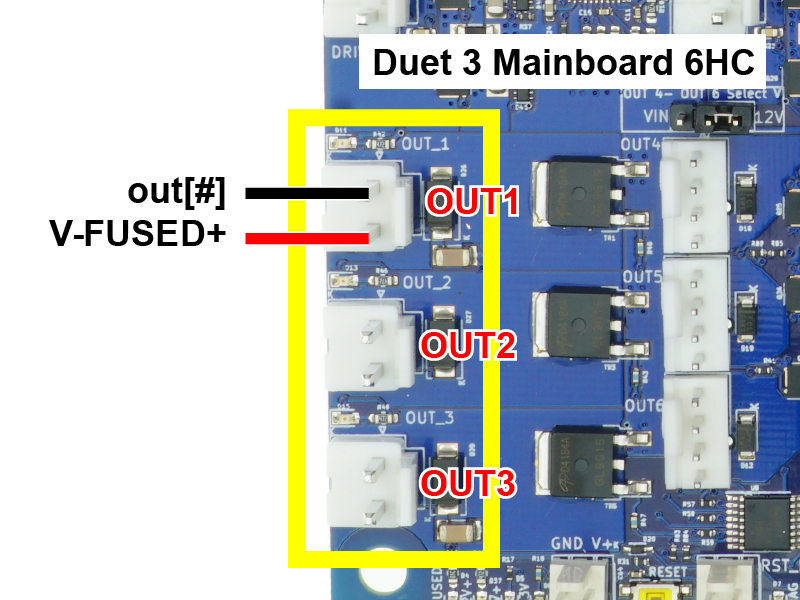
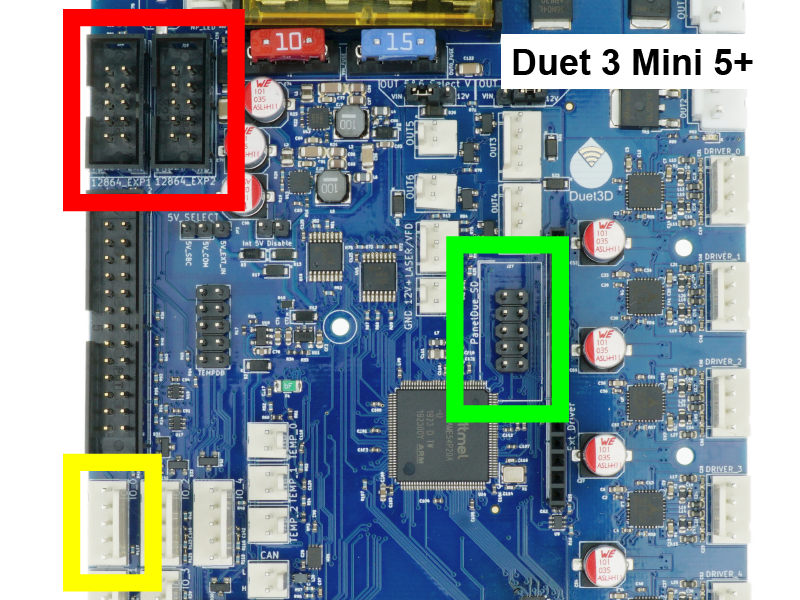
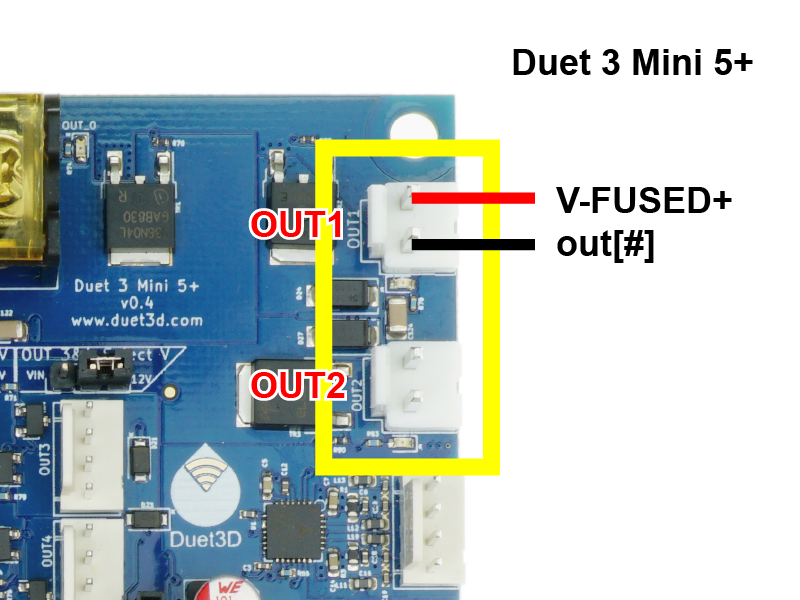 Hotend heaters connect to the pin headers shown in the image, outlined yellow.
Hotend heaters connect to the pin headers shown in the image, outlined yellow.
- JST VH series connectors are used for medium current outputs:
- Duet 3 Mainboard 6HC: used for OUT1, OUT2 and OUT3
- Duet 3 Mini 5+: used for OUT1 and OUT2
- Duet 3 Mainboard 6XD: used for OUT0, OUT1 and OUT2
- Crimp the heater wires to the supplied JST VH crimps, and insert them in the plastic shell, before plugging the heater into the pin headers on the board. See earlier on this page for crimping advice.
- Polarity does not matter for hotend heaters.
- For more details, see User manual: Heaters overview
¶ 14. Stepper motors
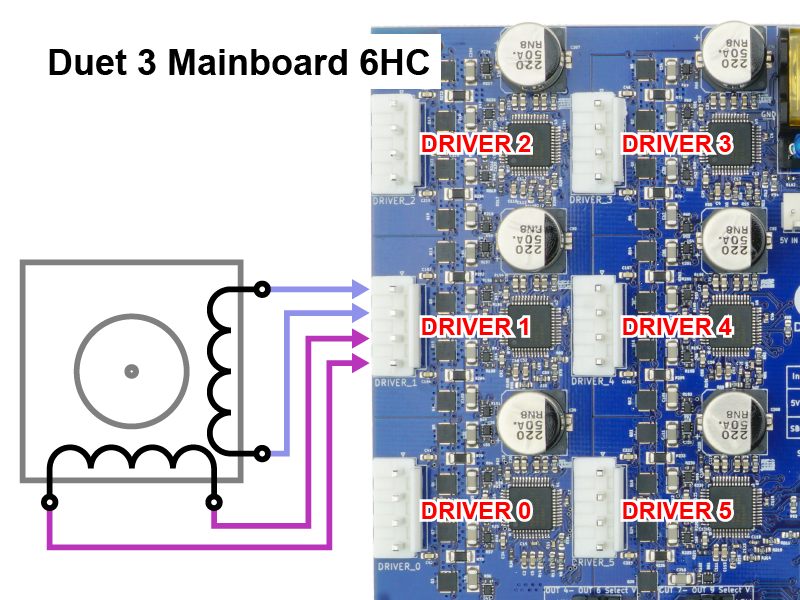
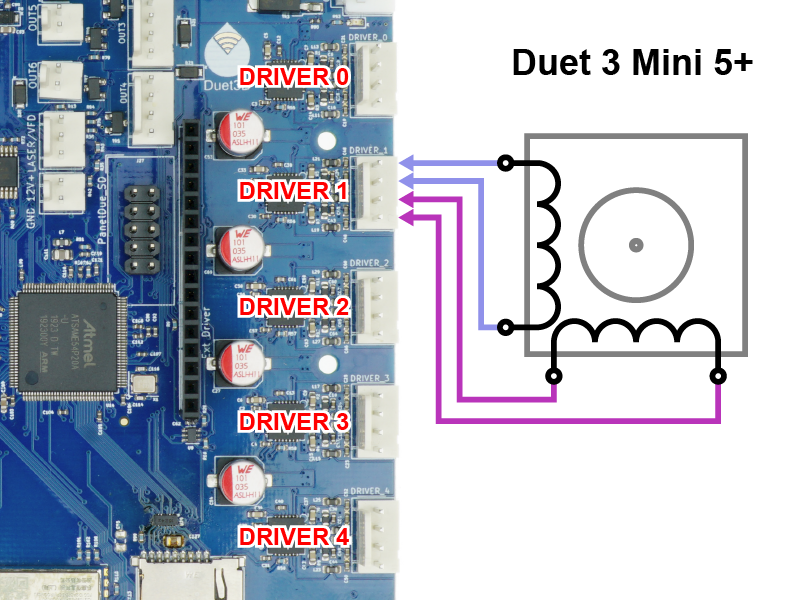 Duet 3 boards have different options to connect stepper motors:
Duet 3 boards have different options to connect stepper motors:
Duet 3 Mainboard 6HC: 6x JST VH 4-pin headers for stepper motors up to 6.3A peak current
Duet 3 Mini 5+: 5x Molex KK-compatible 4-pin headers for stepper motors up to 2A peak current
Duet 3 Mainboard 6XD: 6x Molex KK-compatible 6-pin headers for external stepper or servo motor driver connections
- Motor outputs are labelled DRIVER_0 to DRIVER_5 (6HC, 6XD) or DRIVER_0 to DRIVER_4 (Mini 5+)
- WARNING: For 6HC and Mini 5+, you MUST connect the two wires for one phase of the stepper motor to the two pins at one end of the connector, and the two wires for the other phase to the two pins at the other end (see image above). Incorrectly wiring the stepper motor may result in the failure of the stepper driver on the Duet. Do not assume your stepper motors are wired correctly! Please see User manual: Connecting stepper motors for more details and ways to identify the stepper motor phases.
- Crimp the motor wires to the supplied crimps, and insert them in the plastic shell, before plugging the heater into the pin headers on the board. See earlier on this page for crimping advice.
- For 6XD, see 6XD datasheet: Connecting external motor drivers for details on connecting drivers and motors.
- If you need more stepper motors than available connections, you may use any of the Duet 3 CAN-connected expansion boards. See Duet 3 Family
- For the Mini 5+ there is also a 2x stepper driver expansion board that connects directly to the Mini 5+; for more details see Duet_3_Expansion_Mini_2+.
- For more details, see User manual: Choosing stepper motors
- If you want to run external drivers, see User manual: Connecting external stepper motor drivers.
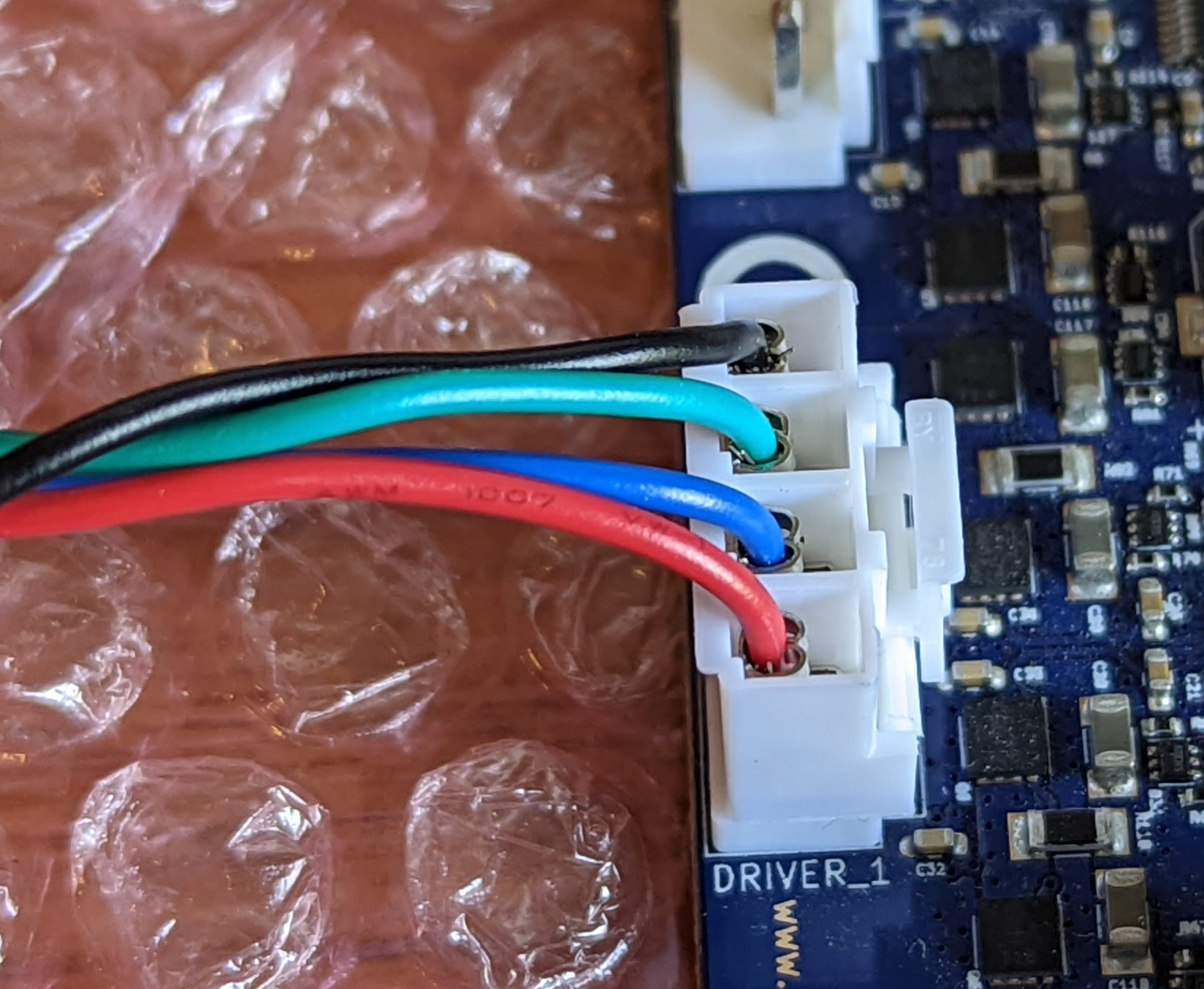
Here is an example of a JST_VH connector:
¶ 15. Connecting a display
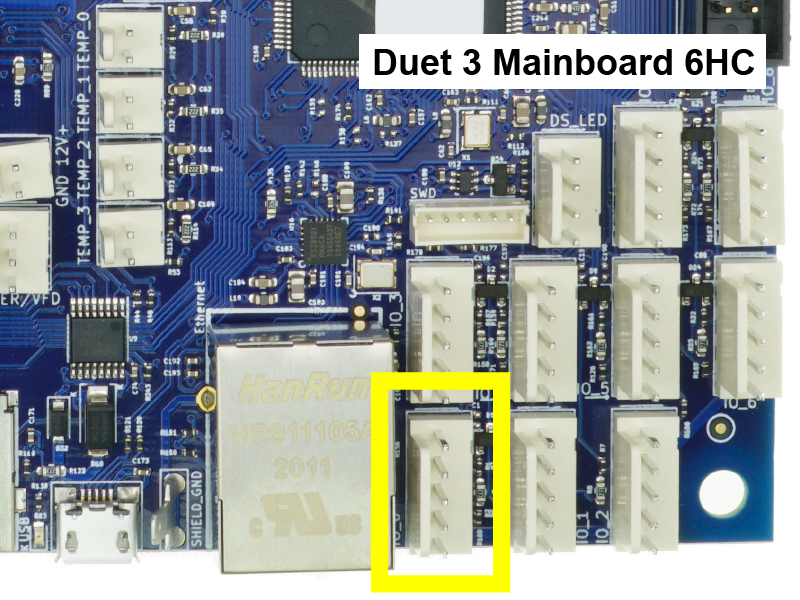
 Two options exist for a directly-connected display for Duet 3 boards.
Two options exist for a directly-connected display for Duet 3 boards.
Connecting a PanelDue
Duet 3 Mainboard 6HC supports PanelDue connected via IO_0 only.
Duet 3 Mainboard 6XD supports PanelDue connected via IO_0 or 10-pin PanelDue_SD connector.
Duet 3 Mini 5+ supports PanelDue connected via IO_0 or 10-pin PanelDue_SD connector
- The PanelDue, an optional accessory sold separately, is a touchscreen display which gives a user the ability to control the Duet with an intuitive interface directly at the printer.
- The PanelDue can be connected in two ways (both cables are supplied with the PanelDue), depending on Duet board:
- A 4-wire cable that contains power and serial signals. This has a maximum recommended length of 1 meter. It plugs into the 5-pin IO_0 header. The supplied 4-wire cable may need to be rewired using the supplied 5-way connector shell; see User manual: Connecting a PanelDue for details.
- a 10-way flat cable with a maximum recommended length of 400mm. It plugs into the 10-pin PanelDue_SD header. It has extra pins that allow the Duet to access the PanelDue's SD card reader. The IO_0 connector cannot be used for other purposes when using the PanelDue_SD header because they share connections.
- For more details, including using the PanelDue_SD header to connect an external SD card reader, see User manual: Connecting a PanelDue.
Connecting a 12864 display
Duet 3 Mini 5+ boards support 12864 mono graphics LCD displays with a rotary encoder. Other Duet 3 boards do not support 12864 displays.
- Duet 3 only supports 12864 displays with the ST7567 controller chip.
- The 12864_EXP1 and 12864_EXP2 connectors are used to connect a 12864 display.
- For details, see User manual: Connecting 12864 displays.
¶ 16. Connecting a Single Board Computer (SBC)
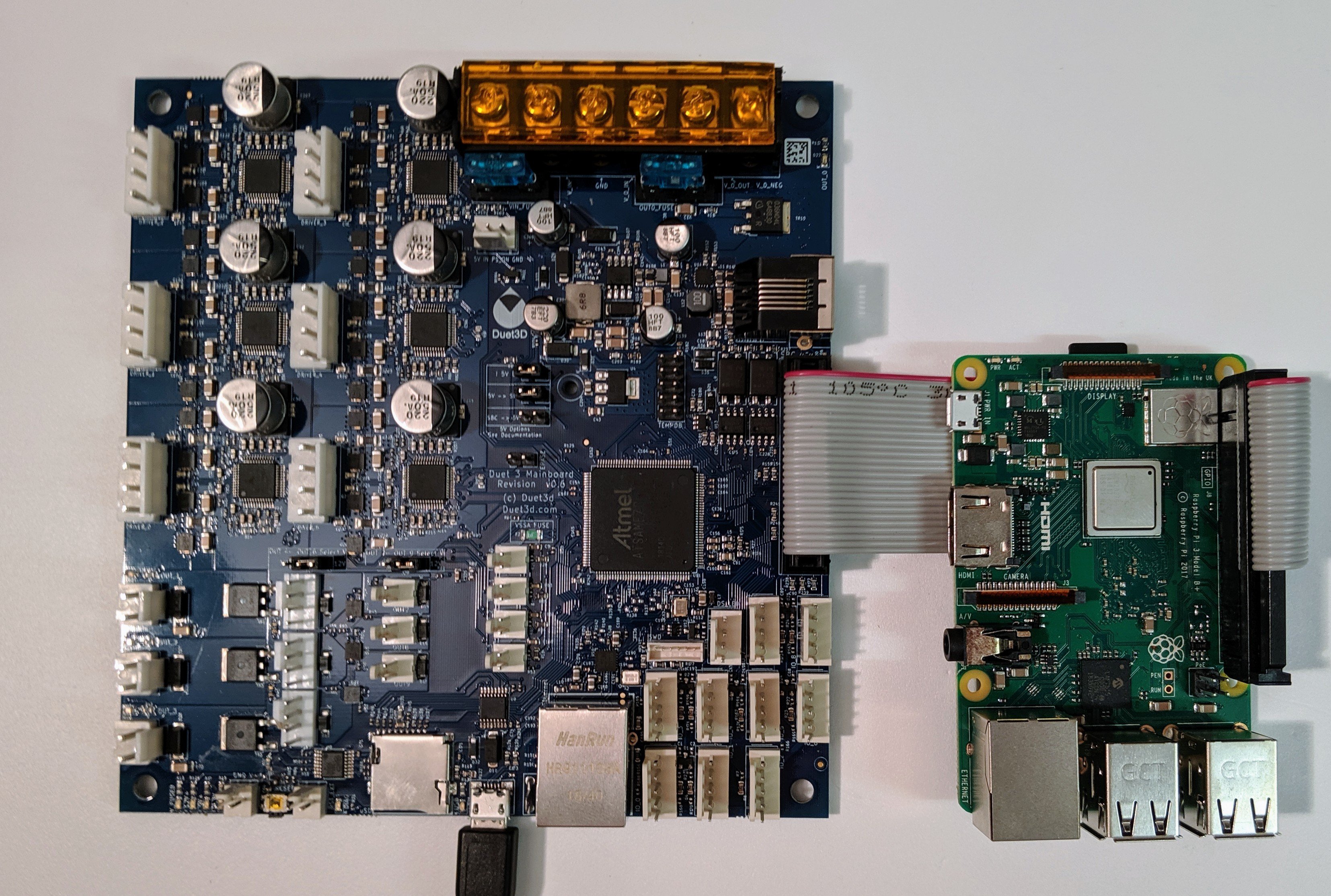
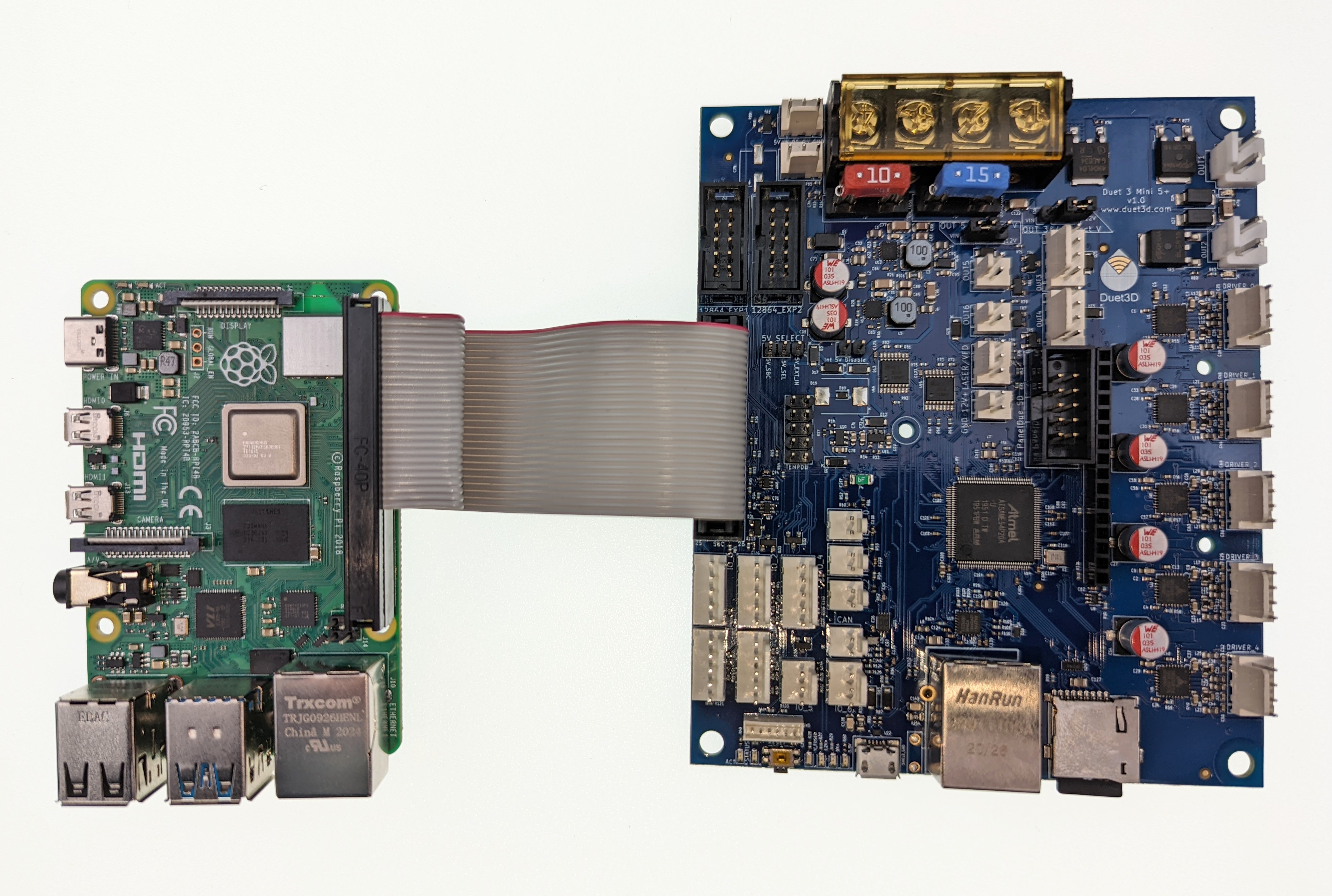 Duet 3 mainboards optionally support connecting a Single Board Computer (SBC) such as a Raspberry Pi.
Duet 3 mainboards optionally support connecting a Single Board Computer (SBC) such as a Raspberry Pi.
- Connect an SBC to the 26-pin SBC header, using the supplied ribbon cable
- Connect the other end to the SBC's GPIO header.
- Note the orientation of the red stripe on the ribbon cable indicating pin 1.
- The cable can be routed around the back of the SBC if necessary, however pin 1 must connect as shown.
- We recommend powering the SBC using it's own PSU, to ensure stable voltage and sufficient supply of current to both Duet and SBC.
- For a detailed guide to setting up Duet in SBC mode, see User manual: Single Board Computer (SBC) setup for Duet 3
¶ 17. Temperature Daughterboard
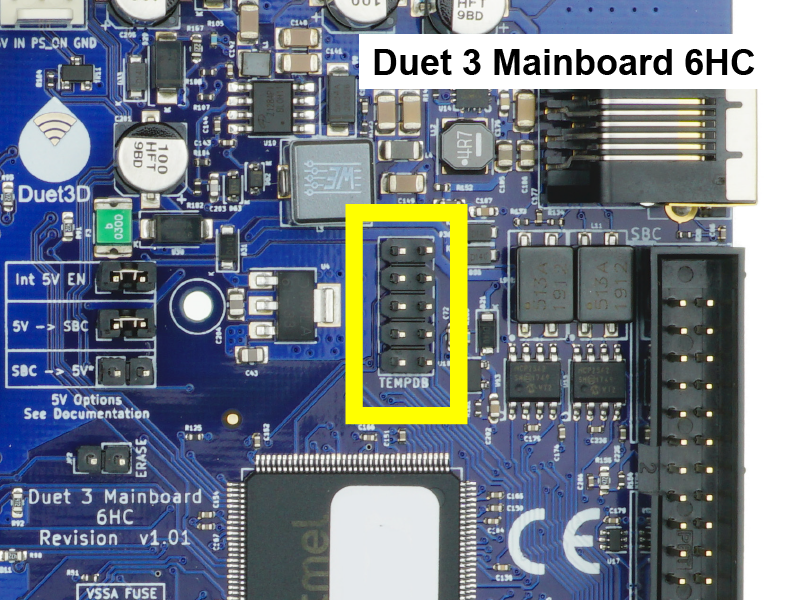
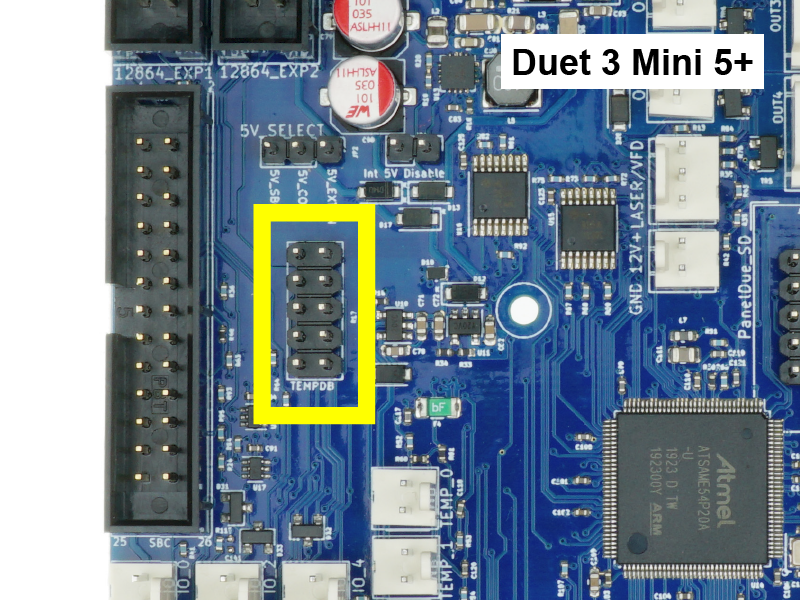 Thermocouples and PT100 temperature sensors send a different signal compared to thermistors and PT1000 temperature sensors, and cannot be connected to the on-board temperature inputs of the Duet.
Thermocouples and PT100 temperature sensors send a different signal compared to thermistors and PT1000 temperature sensors, and cannot be connected to the on-board temperature inputs of the Duet.
- The TEMP_DB connector allows thermocouples or PT100 temperature sensors to be connected to a Duet board, via a Temperature Daughterboard.
- Each daughterboard supports two additional temperature sensors of the same type, ie either 2x PT100 or 2x thermocouple.
- Duet 3 Mainboard 6HC and 6XD support up to two temperature daughterboards (4 channels).
Duet 3 Mini 5+ supports one temperature daughterboard (2 channels) - Thermocouples or PT100 temperature sensors may be desired if, for example, you wish to print with materials which require greater than 290°C, which is the limit of most thermistors. For help selecting temperature sensors to suit your application, see User manual: Choosing temperature sensors
- For more details, see User manual: Connecting thermocouples and User manual: Connecting PT100 temperature sensors
- The temperature daughterboard connector can also be used to connect an accelerometer. For details, see User manual: Connecting an accelerometer
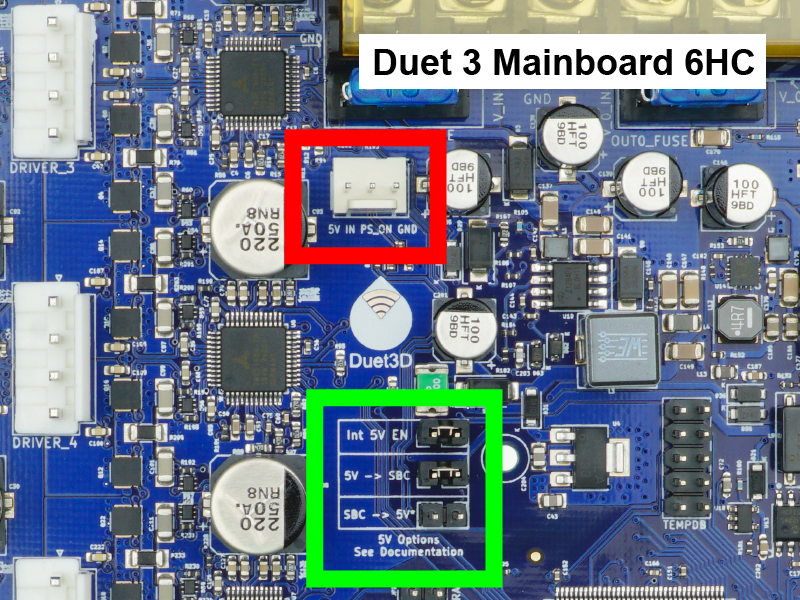
¶ 18. External 5V input and power supply control
- The Duet has an on-board 5V regulator which is powered by the VIN input (12-36V).
- Unless you plan to provide an external 5V source, you should at this time check that there is a jumper on Int 5V EN.
- Optionally, external 5V power can be provided to the board by removing the jumper on Int 5V EN and supplying 5V power to the '5V IN' pin of the EXT_5V connector.
- Duet 3 Mainboard 6HC v1.01 and earlier had jumpers below the 'Int 5V EN' jumper to allow the Duet to supply power to the SBC, or vice versa. Current SBCs (eg Raspberry Pi 4) draw too much power, and we now recommend for both Duet and SBC to be powered separately. 6HC v1.01a boards and later do not have these jumper pins populated. See 6HC hardware overview: 5V for more details.
- The centre pin of the EXT_5V header, labelled
pson, can control an external power supply. The board can be powered from external 5V, with an external supply for VIN turned on and off as required. For more details, see User manual: Power wiring
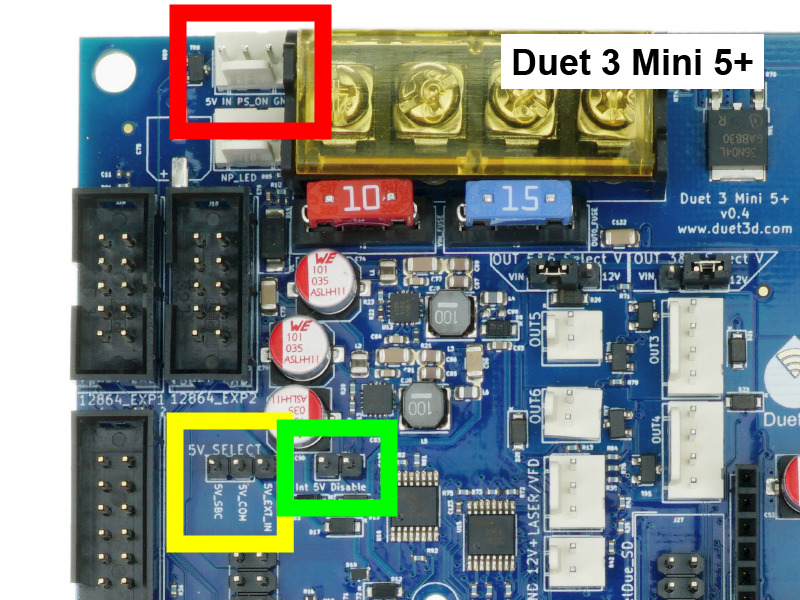
- The Duet has an on-board 5V regulator which is powered by the VIN input (12-24V).
- Unless you plan to provide an external 5V source, you should at this time check that there is no jumper on Int 5V Disable or 5V Select.
- Optionally, external 5V power can be supplied to:
- '5V IN' pin on EXT_5V connector. In this case, add a jumper to the 5V Select jumper between '5V_EXT_IN' and '5V_COM' pins, and add a jumper to Int 5V Disable.
- In some cases you may want to power the Duet from the 5V output of an SBC connected to the SBC header. Note that the total power of the Duet and peripherals must be factored into the SBC power budget, and should not exceed 1A. Powering the SBC from the duet is not supported. In this case, add a jumper to the 5V Select jumper between '5V_SBC' and '5V_COM' pins, and add a jumper to Int 5V Disable.
- The centre pin of the EXT_5V header, labelled
pson, can control an external power supply (note signal shared with io4.out). The board can be powered from external 5V, with an external supply for VIN turned on and off as required. For more details, see User manual: Power wiring
¶ 19. Expansion
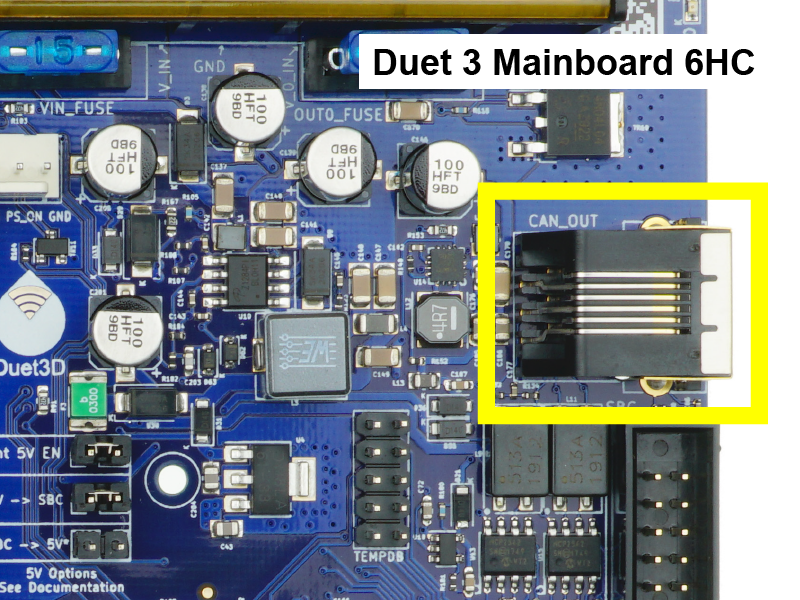
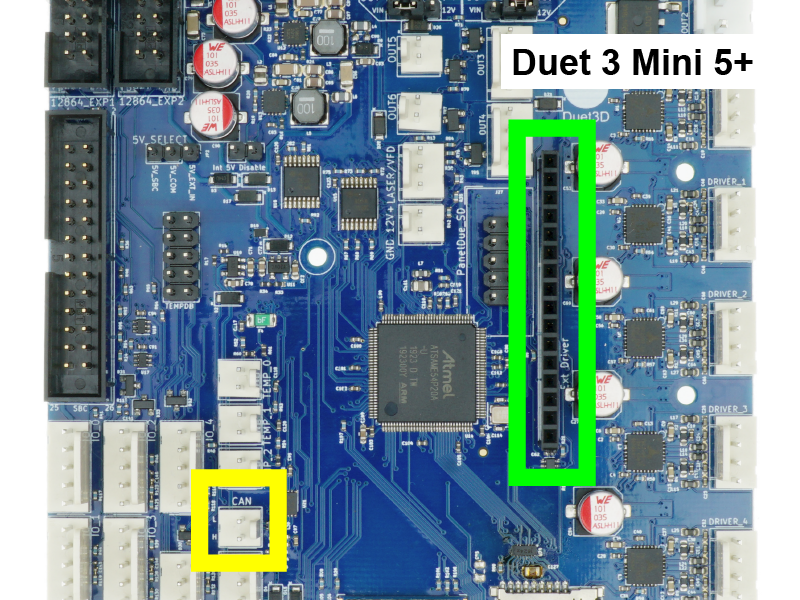 There are a number of options for expanding Duet 3 mainboards beyond their original capabilities.
There are a number of options for expanding Duet 3 mainboards beyond their original capabilities.
CAN-FD Bus
- All Duet 3 boards offer a CAN-FD bus connection, allowing the mainboard to control a wide range of Duet3D manufactured expansion boards.
- Duet 3 Mainboard 6HD and Mainboard 6XD have a RJ11 CAN-FD connector, labelled CAN_OUT
- Duet 3 Mini 5+ has a two-pin CAN header, labelled CAN
- CAN-FD is highly tolerant of noise, is well-supported by modern microcontrollers, and has enough bandwidth to support the high movement command rates needed in 3D printing and other motion control applications.
- For a list of available expansion and tool boards, see Duet 3 family
- For more details on wiring CAN connections, see User manual: CAN connection basics
On-board stepper driver expansion
- The Duet 3 Mini 5+ has an expansion header, labelled Ext Driver, which can be used to control up to two external stepper drivers. Note that signalling levels are 3V. For details see User manual: Connecting external stepper and servo motor drivers
- Duet3D also offer a plug-in expansion board with two extra stepper drivers; for details, see Duet 3 Expansion Mini 2+
¶ 20. WiFi or Ethernet Module
- Duet 3 Mainboard 6HC and Mainboard 6XD are Ethernet only. Duet 3 Mini 5+ comes in WiFi and Ethernet versions.
- The WiFi or Ethernet Module supports a connection over a web interface. It is responsible for the network connection when not using an attached Single Board Computer.
- The WiFi module has a green LED (LED ESP) which indicates WiFi activity; flashing for searching/connecting, on for connected.
- The WiFi module also has a U.FL external antenna connection; don't forget to plug in the external antenna!
- The Ethernet module has two LEDs on the RJ45 housing; Link, which is on when an Ethernet connection is established, and Activity, which flashed whenever data is being actively transferred.
¶ 21. Troubleshooting
If your board does not power up after wiring:
- Check PSU is supplying expected voltage.
- Check for shorts in your wiring between VIN, 12V, 5V, 3.3V and ground (GND).
- Check fuses.
- Disconnect all wiring, check board powers up, then reconnect wiring one connector at time, powering down and back up between each reconnection, to identify wiring that is causing the short circuit.
- Some shorts, eg shorting VIN to 5V or 3.3V, will permanently damage the Duet. Shorting 5V or 3.3V to ground (usually mis-wired endstops) shouldn't cause damage, but will cause the Duet to not boot. See How to destroy your Duet 2, which largely applies to Duet 3 as well.
¶ Wiring Complete!
Congratulations! Your Duet is wired and is ready to configure. Continue to the Configuring firmware guide to configure your Duet!